ICND1 – Router Questions
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two of these functions do routers perform on packets? (Choose two)
A. examine the Layer 2 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the next hops for the packets
B. update the Layer 2 headers of outbound packets with the MAC addresses of the next hops
C. examine the Layer 3 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the next hops for the packets
D. examine the Layer 3 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the complete paths along which the packets will be routed to their ultimate destinations
E. update the Layer 3 headers of outbound packets so that the packets are properly directed to valid next hops
F. update the Layer 3 headers of outbound packets so that the packets are properly directed to their ultimate destinations
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
When packets travel through many routers, the source and destination IP addresses do not change but the source and destination MAC do change.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. An administrator cannot connect from R1 to R2. To troubleshoot this problem, the administrator has entered the command shown in the exhibit. Based on the output shown, what could be the problem?
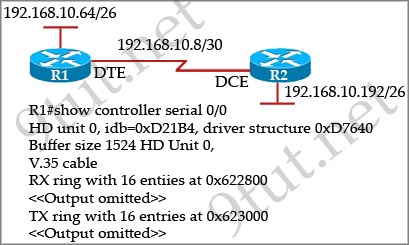
A. The serial interface is configured for half duplex.
B. The serial interface does not have a cable attached.
C. The serial interface has the wrong type of cable attached.
D. The serial interface is configured for the wrong frame size.
E. The serial interface has a full buffer.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The output above is unclear. Normally when we use this command we can see the type of serial connection on this interface, for example “V.35 DCE cable. Below is an example of the same command as above:
|
RouterA#show controllers serial 0 |
Or
|
RouterB#show controllers serial 0 |
but in this case we only get “V.35 cable”. So in fact we are not sure about the answer C. But the output above also does not have any information to confirm other answers are correct or not.
Just for your information, the V.35 male and V.35 female cable are shown below:


Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What two things does a router do when it forwards a packet? (Choose two)
A. switches the packet to the appropriate outgoing interfaces
B. computes the destination host address
C. determines the next hop on the path
D. updates the destination IP address
E. forwards ARP requests
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A network device needs to be installed in the place of the icon labeled Network Device to accommodate a leased line attachment to the Internet. Which network device and interface configuration meets the minimum requirements for this installation?
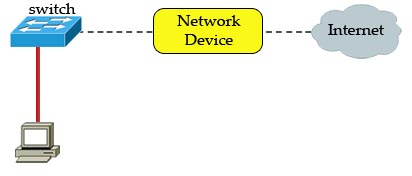
A. a router with two Ethernet interfaces
B. a switch with two Ethernet interfaces
C. a router with one Ethernet and one serial interface
D. a switch with one Ethernet and one serial interface
E. a router with one Ethernet and one modem interface
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two commands will display the current IP address and basic Layer 1 and 2 status of an interface? (Choose two)
A. Router#show version
B. Router#show ip interface
C. router#show protocols
D. router#show controllers
E. Router#show running-config
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
The outputs of “show protocols” and “show ip interface” are shown below:
| Global values: Internet Protocol routing is enabled Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is down Internet address is 10.1.1.1/30 Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down Internet address is 209.65.200.225/30 Serial0/2 is up, line protocol is down Serial0/3 is up, line protocol is down NVI0 is up, line protocol is up Interface is unnumbered. Using address of NVI0 (0.0.0.0) Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is 10.1.10.1/32 Loopback1 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is 10.1.2.1/27 Loopback6 is up, line protocol is up |
| Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is down Internet address is 10.1.1.1/30 Broadcast address is 255.255.255.255 Address determined by non-volatile memory MTU is 1500 bytes Helper address is not set Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled Multicast reserved groups joined: 224.0.0.5 Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is not set Proxy ARP is enabled Local Proxy ARP is disabled Security level is default Split horizon is disabled ICMP redirects are always sent ICMP unreachables are always sent ICMP mask replies are never sent IP fast switching is enabled IP fast switching on the same interface is enabled IP Flow switching is disabled IP CEF switching is disabled IP Feature Fast switching turbo vector IP multicast fast switching is enabled IP multicast distributed fast switching is disabled IP route-cache flags are Fast Router Discovery is disabled IP output packet accounting is disabled IP access violation accounting is disabled TCP/IP header compression is disabled RTP/IP header compression is disabled Policy routing is disabled Network address translation is enabled, interface in domain inside BGP Policy Mapping is disabled WCCP Redirect outbound is disabled WCCP Redirect inbound is disabled WCCP Redirect exclude is disabled |
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. If the resume command is entered after the sequence that is shown in the exhibit, which router prompt will be displayed?
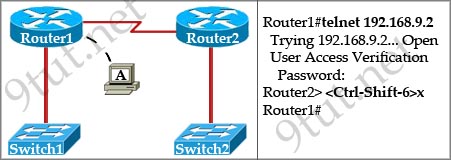
A. Router1>
B. Router1#
C. Router2>
D. Router2#
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The “Ctrl-Shift-6” and “x” is used to suspend the telnet session. In this case, the telnet session from Router1 to Router2 will be suspended.
If we enter the keyword “resume”, Router1 will try to resume the telnet session to Router2 (you will see the line [Resuming connection 1 to 192.168.9.2 … ]) and we will get back the Router2> prompt.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]When a router makes a routing decision for a packet that is received from one network and destined to another, which portion of the packet does if replace?
A. Layer 2 frame header and trailer
B. Layer 3 IP address
C. Layer 5 session
D. Layer 4 protocol
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The Layer 2 information (source and destination MAC) would be changed when passing through each router. The Layer 3 information (source and destination IP addresses) remains unchanged.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two of these functions do routers perform on packets? (Choose two)
A. examine the Layer 2 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the next hops for the packets
B. update the Layer 2 headers of outbound packets with the MAC addresses of the next hops
C. examine the Layer 3 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the next hops for the packets
D. examine the Layer 3 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the complete paths along which the packets will be routed to their ultimate destinations
E. update the Layer 3 headers of outbound packets so that the packets are properly directed to valid next hops
F. update the Layer 3 headers of outbound packets so that the packets are properly directed to their ultimate destinations
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
When packets travel through many routers, the source and destination IP addresses do not change but the source and destination MAC do change.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]How do you bypass password on Cisco device?
A. Change the configuration register to 0x2142
B. Reset the device
C. Unplug and plug the power
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Change the configuration register to 0x2142. With this setting when that router reboots, it bypasses the startup-config and no password is required.
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which router command can be used to determine the status of Serial 0/0?
A. show ip route
B. show interfaces
C. show s0/0 status
D. debug s0/0
E. show run
F. show version
Answer: B[/am4show]


Hi, can anyone email me ICND-1 Dump please ? email me at {email not allowed}
What really is the answer for Q5??
I also think that “show IP interface” is the answer. I’m not sure why; But I tried C&D on Q5 on the exam and got 100% in all categories except “Network device security”. And I’m Pretty sure that this question doesn’t fall on that category. So for everyone arguing with the answer, just check it out yourself. Cheers!
B C
B and C
Thanks @ Makky the 285q are still valid
Confirming 285q dumps are still good
send me reading material {email not allowed}
HOW TO CHANGE ROUTER CONFIGURATION PASSWORD…???
is these all questions form 2017?