ICND2 – RSTP
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: If you are not sure about Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol, please read our Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol RSTP Tutorial.
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three statements about RSTP are true? (Choose three)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconvening time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expands the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
E. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
F. RSTP uses the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
Answer: A B D[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
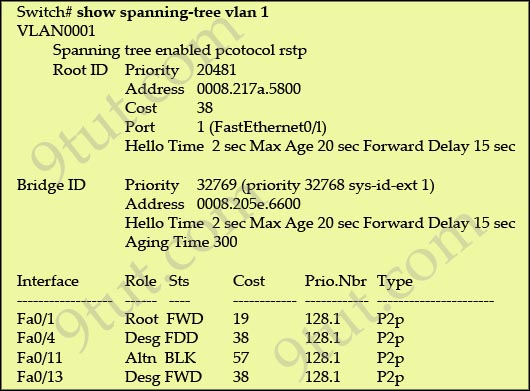
Why has this switch not been elected the root bridge for VLAN1?
A. It has more than one internee that is connected to the root network segment.
B. It is running RSTP while the elected root bridge is running 802.1d spanning tree.
C. It has a higher MAC address than the elected root bridge.
D. It has a higher bridge ID than the elected root bridge.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
As we can see from the output above, the priority of the root bridge is 20481 while that of the local bridge is 32769.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command enables RSTP on a switch?
A. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
B. spanning-tree uplinkfast
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true?
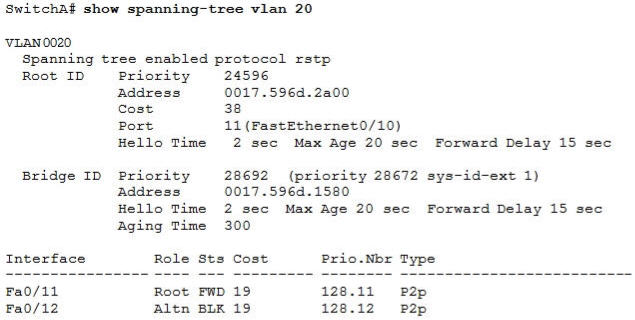
A. The Fa0/11 role confirms that SwitchA is the root bridge for VLAN 20.
B. VLAN 20 is running the Per VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol.
C. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.1580.
D. SwitchA is not the root bridge, because not all of the interface roles are designated.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Only non-root bridge can have root port. Fa0/11 is the root port so we can confirm this switch is not the root bridge -> A is not correct.
From the output we learn this switch is running Rapid STP, not PVST -> B is not correct.
0017.596d.1580 is the MAC address of this switch, not of the root bridge. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.2a00 -> C is not correct.
All of the interface roles of the root bridge are designated. SwitchA has one Root port and 1 Alternative port so it is not the root bridge -> D is correct.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The output that is shown is generated at a switch. Which three of these statements are true? (Choose three)
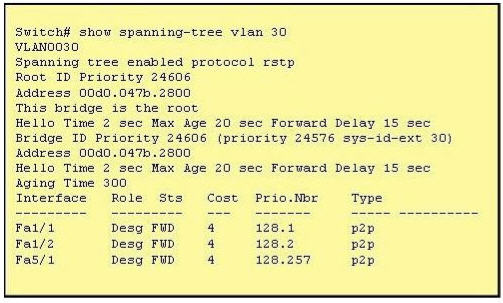
A. All ports will be in a state of discarding, learning or forwarding.
B. Thirty VLANs have been configured on this switch.
C. The bridge priority is lower than the default value for spanning tree.
D. All interfaces that are shown are on shared media.
E. All designated ports are in a forwarding state.
F. The switch must be the root bridge for all VLANs on this switch.
Answer: A C E[/am4show]
Explanation
From the output, we see that all ports are in Designated role (forwarding state) -> A and E are correct.
The command “show spanning-tree vlan 30″ only shows us information about VLAN 30. We don’t know how many VLAN exists in this switch -> B is not correct.
The bridge priority of this switch is 24606 which is lower than the default value bridge priority 32768 -> C is correct.
All three interfaces on this switch have the connection type “p2p”, which means Point-to-point environment – not a shared media -> D is not correct.
The only thing we can specify is this switch is the root bridge for VLAN 3o but we can not guarantee it is also the root bridge for other VLANs -> F is not correct.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)
A. blocking
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
Answer: A D[/am4show]
Explanation
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding but the answers don’t mention about discarding state so blocking state (answer A) may be considered the best alternative answer.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two)
A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: B E[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
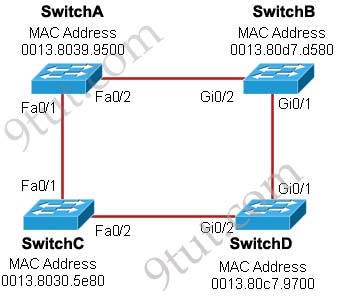
A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F[/am4show]
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.
Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the “cost to the root bridge” of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
In the exhibit you also see FastEthernet port is connecting to GigabitEthernet port. In this case GigabitEthernet port will operate as a FastEthernet port so the link can be considered as FastEthernet to FastEthernet connection.
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again

SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 19 (the cost value of 100Mbps link although the port on Switch D is GigabitEthernet port) and advertises this value (19) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 23. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 38 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port -> D is not correct.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:
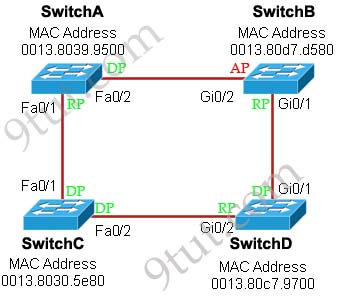
+ DP: Designated Port (forwarding state)
+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. At the end of an RSTP election process, which access layer switch port will assume the discarding role?
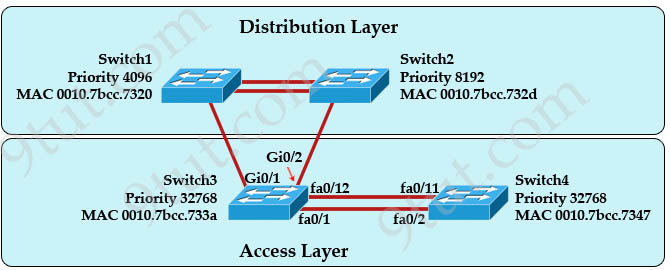
A. Switch3, port fa0/1
B. Switch3, port fa0/12
C. Switch4, port fa0/11
D. Switch4, port fa0/2
E. Switch3, port Gi0/1
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
In this question, we only care about the Access Layer switches (Switch3 & 4). Switch 3 has a lower bridge ID than Switch 4 (because the MAC of Switch3 is smaller than that of Switch4) so both ports of Switch3 will be in forwarding state. The alternative port will surely belong to Switch4.
Switch4 will need to block one of its ports to avoid a bridging loop between the two switches. But how does Switch4 select its blocked port? Well, the answer is based on the BPDUs it receives from Switch3. A BPDU is superior than another if it has:
1. A lower Root Bridge ID
2. A lower path cost to the Root
3. A lower Sending Bridge ID
4. A lower Sending Port ID
These four parameters are examined in order. In this specific case, all the BPDUs sent by Sswitch3 have the same Root Bridge ID, the same path cost to the Root and the same Sending Bridge ID. The only parameter left to select the best one is the Sending Port ID (Port ID = port priority + port index). In this case the port priorities are equal because they use the default value, so Switch4 will compare port index values, which are unique to each port on the switch, and because Fa0/12 is inferior to Fa0/1, Switch4 will select the port connected with Fa0/1 (of Switch3) as its root port and block the other port -> Port fa0/11 of Switch4 will be blocked (discarding role).
If you are still not sure about this question, please read my RSTP tutorial.


good job 9tut thank you
Great job 9tut!
One thing I’ve noticed, question one should state ‘Recovering’ instead of ‘reconvening’ for answer A.
Make that Reconverging 😉
The answer to question 6 is incorrect.
B. learning
D. forwarding
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding (NO blocking!).
In Q8 the cost of the link between Switch A and Switch B should be 19 because Fa0/2 on Switch A would drop the link speed to 100Mbps on Switch B Gi0/2. Right? If so, the same would apply to Switch C and Switch D.
To Dan
It will still go to discarding/ forward until a timer runs out and it re checks the network.
I see the key word is “converged” but you can’t provide wrong answer as a choice. I am sure this was worded incorrectly and not really like this under test.
To Dan
The word is more correct . I think
I passed icnd2 today thanks 9tut
I know the answer in Q8 is correct, but I don’t understand why the cost on Gi0/1 is 8 and Gi0/2 is 23? From Switch C Fa0/1 to Switch A fa0/1 the cost is 19 as they are both fastethenet port and the link speed is 100mbps, however from Switch A Fa0/2 to Switch B Gi0/2 the cost should be 19 as well, as one of the port is fastethernet and the max link speed is 100mbps, even the Gi0/2 support 1GBPs it will still be a 100mbps link, is that right? thanks !
@John, you are correct. The answer to Q8 is correct but the diagram they used to explain it is incorrect. From Switch B to Switch A the cost would be 19, and the same thing with Switch D to Switch C when they have it labeled as 4 for some reason. So From Switch B it would choose G0/1 because the cost would be 23 (19+4) as apposed to 38 (19+19) if it went out of G0/2.
@Ben Slazen Thanks for clear things up
Thanks guys for clearing things up about Q8 – Ive 1 last question. the link between SA and SB, why they are comparing Mac addresses. I thought you go for the Mac address when there is a tie in the cost. You help is appreciated.
Terry
Got Q6,Q8 and Q10 today.
get dumps with nuggets free from this following link
wurl. cc/dumps
Just took the test today – 980/1000 ALL 9 questions from this page came in my test. Thanks 9tuts! Also got Frame Relay, EIGRP and OSPF labs
THERE IS NO NEED FOR ANY DUMPS – just study one book (Wendel or Todd) and the you tube lessons available free for visual knowledge. Along with 9tuts these are enough for 900 and over marks with ease.
But you MUST understand the concepts and not mug up the answer as they change the options and answers
@all: We had to move all the questions and answers out of 9tut. We can only keep the explanation. You can download the questions and answers at: https://mega.co.nz/#!oIdESYbD!yyu33vygrfKPy4rcmcbV6qW2fxINNoTokuDM3CjA_og
@Terry, you’re right.
From Odom’s Official Cert Guide: “For switches connected to the same LAN segment, the switch with the lowest cost to reach the root, *as advertised in the hello they send on the link*, becomes the DP on that link. In the case of a tie, among the switches that tied on cost, the switch with the lowest BID becomes the DP.”
Swich B g0/2 should dp instead of swtch A fas0/2 since it advertise better BPDU On to segment
It will be selected Dp if only cost is a tie it has lower mac address compared to B
Had question 6 today, which is now corrected to discarding instead of the wrong choice blocking
For question 8 ,
the answer is correct
the segment betwn switch A and Switch B
the cost from A to root is 19
while cost from B to root is 4 + 19 = 23
so the one will lower cost will be assigned the DP
and the high cost will be assigned the AP
Thats how we get option A as the right answer
is there any problem with the page?
i can’t see the Questions an answers.
e.g.
Note: If you are not sure about Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol, please read our Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol RSTP Tutorial.
Question 1
Question 2
Explanation
As we can see from the output above, the priority of the root bridge is 20481 while that of the local bridge is 32769.
Question 3
Question 4
Explanation
Only non-root bridge can have root port. Fa0/11 is the root port so we can confirm this switch is not the root bridge -> A is not correct.
From the output we learn this switch is running Rapid STP, not PVST -> B is not correct.
0017.596d.1580 is the MAC address of this switch, not of the root bridge. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.2a00 -> C is not correct.
All of the interface roles of the root bridge are designated. SwitchA has one Root port and 1 Alternative port so it is not the root bridge -> D is correct.
Question 5
Explanation
@mikis: Because of copyrighted issues, 9tut had to remove all questions and answers. You can download them at: https://mega.co.nz/#!oIdESYbD!yyu33vygrfKPy4rcmcbV6qW2fxINNoTokuDM3CjA_og
@Train thank you!
since u had to delete the Q&A, thanku for providing all the information on the link .
https://mega.co.nz/#!oIdESYbD!yyu33vygrfKPy4rcmcbV6qW2fxINNoTokuDM3CjA_og
How can the answer to question 8 be correct… for the links to work correctly they must autonegotiate the link speed (bandwith) to 100mbps. So the explanation done for this question isnt really how it should be if you ask me…
The switch considers its local cost to reach the root and with a link that has a 100mbps vs 1000mbps for the link to work it should auto negotiate the lowest link speed. what would result in a cost of 19…
WellIknowbetter?,
Upon receipt of the technology abilities of the other device, both devices decide the best possible mode of operation supported by both devices per link. The link between SwitchA FA0/2 and SwitchB Gi0/2 autonegotiates to the best mode of operation that both support, 100mbps. The link between SwitchB Gi0/1 and SwitchD Gi0/1 autonegotiates to 1000mbps, the best possible operation mode between those two. This makes the cost of the Fa link 19 and the Gi link 4, making the Gi link the better path to the Root Bridge.
Q9 : because Fa0/12 is inferior to Fa0/1…………..when 12 is inferior of 1
How many RSTP questions are actually on the test since the ICND II published by ODOM book skips over this entirely?
@Snivel….Good point. I just checked my book and there is only 3 short paragraphs about RSTP on pages 38-39.
Are the questions still valid?
The RSTP questions seems to be broken. Cannot accessed it
Yeah I’m a premium member
https://www.9tut.net/final_flash/ICND2/RSTP/quiz.html
Q5: Can someone explain why “A” is a correct answer ? thankyou
For question 8 ,
the answer A is NOT correct!!
the segment betwn switch A and Switch B
the cost from A to root (Switch C) is 19
while cost from B to root is 4 + 4 (switch B -> Gig 0/1 (cost 4) and Switch D -> Gi 0/2 (Cost 4) = 8
so the one will lower cost will be assigned the DP
and the high cost will be assigned the AP
A is NOT correct!!
Can someone explain why Answer A is correct?
I tried this out on packet Tracer and it is correct yet I don’t understand as I thought it only went with the lower MAC address if the cost to the root was the same either way?
But it is not?
Q.8
Sanity Check!!!!
Would the links speeds between Switch A and B And Switch C and D not be 100mbps? Giving you a cost of 19 on each link?
A Fast Ethernet port and a Gig Ethernet port on the same link would only give you a max bandwidth of 100mbps as the Gig port would have to run at 100mbps to work.
Let me know as this is driving me up the wall!!
Thanks
@9tut
Question 8:
as @wompers, @CherryBob and several others stated: a Gi interface cannot connect to an Fa Interface with 1000mbps! So this connection between sw d and sw c (same between sw b and sw a) must have cost of 19 and not 4!!!
Or where is the fault in thinking?? Or does RSTP know better?! 😉
This should be found out soon!!
@9tut
comment not accepted?! I try again!
@9tut
question 8:
I’ve just found the right explanation at WWW 9tut com in the RSTP section!
You should copy+paste it here!!
Anyway: great job of 9tut and always worth 9$!! Thanks a lot!
@9tut
question 8: I’m talking about the CCNA section and the explained RSTP questions there!
@PaulV: Thanks for your detection. We have just updated the explanation of Q.8
Took ICND2 today passed (825) passing score . must of the Q was on there. Thanks 9TUT
someone help me get a vce player?
Just tested today, Q6 has been updated. Answers are now discarding and forwarding.
9tut your answers are correct for Q8 and Q9 but your explanations are not. RSTP and STP only use the MAC address to work out DP ports if the costs are the same. In a triangle topology where the top switch is the root and both bottom switches had the same cost (eg FastEthernet) to the RB THEN you would use Mac addresses. Since both of those topologies dont have that then in Q8 SW A has a better COST than SW B so therefore SW A port in that segment will be DP and SW B port will be the AP or blocked (discarding). Sw B GI0/1 will be its root.
In Q9 SW1 is the RB therefore SW3 will have a better cost to the RB than SW4 which makes both its ports DP. SW4 then has to decide which port will be blocked. As both ports have the same BID (MACs are the same) it to revert to the highest port number being blocked.
For Q5 could you give more explanations :
A is wrong ? -> Switch is root so port will only have Desg/FWD role/state
B is wrong
C is correct
D is wrong
E is correct
F is correct ? -> all switch are running rstp, not pvst
I think C,E,F is correct
Polu,
The output is showing for VLAN 30. There could be more VLANs on the switch. Therefore, F is not necessarily right. Also, it is possible to have different root bridges for each VLAN.
Q5+++
Polu, it says refer to the exhibit, from the exhibit it only visualizes forwarding state.
i think like that.
Visit https://www.dumps4download.us/free-200-101/cisco-question-answers.html this link and get free Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 200-101 exam sample questions.
@Salene the exam changed last year