ICND2 – IP Routing Questions
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]If host Z needs to send data through router R1 to a storage server, which destination MAC address does host Z use to transmit packets?
A. the host Z MAC address
B. the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to the storage server
C. the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to host Z
D. the MAC address of the storage server interface
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Host Z will use ARP to get the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to it and use this MAC as the destination MAC address. It use the IP address of the storage server as the destination IP address.
For example in the topology below, host A will use the MAC address of E0 interface of the router as its destination MAC address to reach the Email Server.
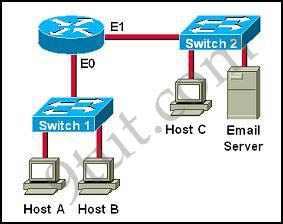
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. RTA is configured with a basic configuration. The link between the two routers is operational and no routing protocols are configured on either router. The line shown in the exhibit is then added to router RTA. Should interface Fa0/0 on router RTB shut down, what effect will the shutdown have on router RTA?
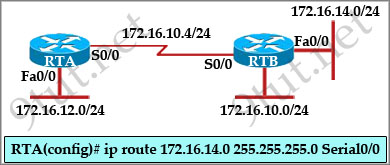
A. A route to 172.16.14.0/24 will remain in the RTA routing table.
B. A packet to host 172.16.14.225 will be dropped by router RTA
C. Router RTA will send an ICMP packet to attempt to verify the route.
D. Because router RTB will send a poison reverse packet to router RTA, RTA will remove the route.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Static routes remain in the routing table even if the specified gateway becomes unavailable. If the specified gateway becomes unavailable, you need to remove the static route from the routing table manually. However, static routes are removed from the routing table if the specified interface goes down, and are reinstated when the interface comes back up.
Therefore the static route will only be removed from the routing table if the S0/0 interface on RTA is shutdown.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asa/asa84/configuration/guide/route_static.html)
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]A router is running three routing processes: RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP, each configured with default characteristics. Each process learns a route to the same remote network.
If there are no static routes to the destination and none of the routes were redistributed, which route will be placed in the IP routing table?
A. the route learned through EIGRP
B. the route learned through OSPF
C. the route learned through RIP
D. the route with the lowest metric
E. all three routes with the router load balancing
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which parameter would you tune to affect the selection of a static route as a backup, when a dynamic protocol is also being used?
A. hop count
B. administrative distance
C. link bandwidth
D. link delay
E. link cost
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
By default a static route has the Administrative Distance (AD) of 1, which is always preferred to dynamic routing protocols. In some cases we may want to use dynamic routing protocols and set static routes as a backup route when the “dynamic” routes fail -> we can increase the AD of that static route to a higher value than the AD of the dynamic routing protocols.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]A router receives information about network 192.168.10.0/24 from multiple sources. What will the router consider the most reliable information about the path to that network?
A. an OSPF update for network 192.168.0.0/16
B. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24
C. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24 with a local serial interface configured as the next hop
D. a RIP update for network 192.168.10.0/24
E. a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
F. a default route with a next hop address of 192.168.10.1
Answer: E[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement is true, as relates to classful or classless routing?
A. RIPV1 and OSPF are classless routing protocols.
B. Classful routing protocols send the subnet mask in routing updates.
C. Automatic summarization at classful boundaries can cause problems on discontigous networks.
D. EIGRP and OSPF are classful routing protocols and summarize routes by default.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Discontiguous networks are networks that have subnets of a major network separated by a different major network. Below is an example of discontiguous networks where subnets 10.10.1.0/24 and 10.10.2.0/24 are separated by a 2.0.0.0/8 network.
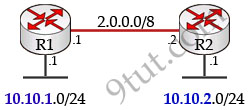
If we configure automatic summarization at classful boundaries, users on network 10.10.1.0/24 cannot communicate with users on network 10.10.2.0/24.
If you are not clear about automatic summarization please read the last part of this tutorial: http://www.9tut.com/eigrp-routing-protocol-tutorial.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two are advantages of static routing when compared to dynamic routing? (Choose two)
A. Security increases because only the network administrator may change the routing tables.
B. Configuration complexity decreases as network size increases.
C. Routing updates are automatically sent to neighbors.
D. Route summarization is computed automatically by the router.
E. Routing traffic load is reduced when used in stub network links.
F. An efficient algorithm is used to build routing tables using automatic updates.
G. Routing tables adapt automatically to topology changes.
Answer: A E[/am4show]
Explanation
Static routing can only be configured for each route manually so it is more secure than dynamic routing which only needs to declare which networks to run -> A is correct.
Also static route does not use any complex algorithm to find out the best path so no routing updates need to be sent out -> reduce routing traffic load. Static routing is useful especially in stub network links.
Note: Stub network (or stub router) is used to describe a network (or router) that does not have any information about other networks except a default route. This type of network (or router) usually has only one connection to the outside.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]A technician pastes the configurations in the exhibit into the two new routers shown. Otherwise, the routers are configured with their default configurations. A ping from Host1 to Host2 fails, but the technician is able to ping the S0/0 interface of R2 from Host1. The configurations of the hosts have been verified as correct. What is the cause of the problem?
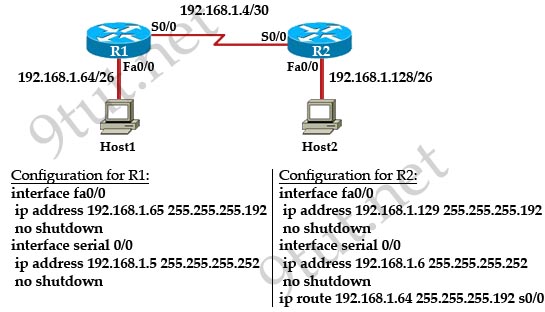
A. The serial cable on R1 needs to be replaced.
B. The interfaces on R2 are not configured properly.
C. R1 has no route to the 192.168.1.128 network.
D. The IP addressing scheme has overlapping subnetworks.
E. The ip subnet-zero command must be configured on both routers.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Host1 can ping the Serial interface of R2 because R1 has the network of 192.168.1.4/30 as directly connected route. But R1 does not know how to route to the network of Host2 (192.168.1.128/26) so R1 will drop that ping without trying to send it out S0/0 interface. To make the ping work, we have to configure a route pointing to that network (for example: ip route 192.168.1.128 255.255.255.192 s0/0 on R1).
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]How does a router handle an incoming packet whose destination network is missing from the Routing table?
A. It discards the packet.
B. It broadcasts the packet to each network on the router.
C. It routes the packet to the default route.
D. It broadcasts the packet to each interface on the router.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are two drawbacks of implementing a link-state routing protocol? (Choose two)
A. the sequencing and acknowledgment of link-state packets
B. the requirement for a hierarchical IP addressing scheme for optimal functionality
C. the high volume of link-state advertisements in a converged network
D. the high demand on router resources to run the link-state routing algorithm
E. the large size of the topology table listing all advertised routes in the converged network
Answer: B D[/am4show]


Why would the answer to question 2 not be B? If the interface is shut down as the question said, I thought the route is removed until the interface is reinstated. In that case, why wouldn’t RTA just drop the packet because it would not have the route from RTB anymore?
Nevermind, I just realized the error in my thinking.
can someone elaborate the answer to question 9?
is this still updated?
Question 9
A. It discards the packet.
If the router has the default gateway defined, then this route will also be present in the routing table, thus by saying that this destination network is missing from the routing table would imply answer A, since the router sends an icmp message for the source and drops the package.
I do not understand why at question 9 the answer is C.
We don’t know if there is configure a default route or not. I think is not configured. So, if there is no default route, the correct answer is A. If the default route was configured, then yes, answer C is correct.
At the second thought … I really don’t know what is the correct answer. :))
9tut Please answer the question 9
I think that the answer is A->”It discards the packet” because not in any time the default route is configured and i think the question is talk usually about on the default case
@Paz: We are not sure about Q.9 either as Cisco did not indicate if there is a default route configured or not.
please what do they mean by configure a static route using an intermediate address
The answer to question# 9 is A
Personally I think Q. 9 is a bit of a trick question. It states, “whose destination network is missing”. To me this means there is no configuration whatsoever in the routing table, including default route, that tells the packet where to go. In that case it would be discarded. If there were a default route, then yes, it would be sent to default route. You can’t presume anything into the question if it isn’t stated in the question.
In question 9. if there is a default route then the router will forward the packet to the default route. Therefore, option c is correct, not option A.
We have to know if there is a a default route set. You cant just assume one is there. No route discard packets. Q 9 is a trick question
@9tut, please clarify Q9.
It says “whose destination network is missing”, it does not talk about the default gateway. The default gateway is no the destination network, never is. The TCP packet has, among other things, source and destination. If the destination is missing the packet is sent to the default gateway. C should be the correct answer. (I check with networking guys)
Q9.
Everybody is right, but the question leads to too many intepretations. 9tuts comments are spot on.
Please someone can explain Question 5? Why the answer is E.
a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
Anonymous August 19th, 2019
Please someone can explain Question 5? Why the answer is E.
a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
I am pasting a link to explaing – https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/enhanced-interior-gateway-routing-protocol-eigrp/8651-21.html
This link shows the Default Administrative Distance of routes in a routing table. Connected Routes are 0 The ranges for Administrative Distance is 0 – 255 0 being the most reliable.
Connected 0
Static 1
eBGP 20
EIGRP (internal) 90
IGRP 100
OSPF 110
IS-IS 115
RIP 120
EIGRP (external) 170
iBGP 200
EIGRP summary route 5