ICND2 – Troubleshooting Questions
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two pieces of information are provided by the “show controllers serial 0” command? (Choose two)
A. the type of cable that is connected to the interface.
B. The uptime of the interface
C. the status of the physical layer of the interface
D. the full configuration of the interface
E. the interface’s duplex settings
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Explanation
Below is an example of the output of this command:
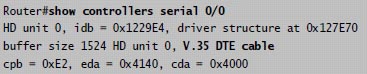
The “show controllers serial …” command tells us about the type of the cable (in the case V.35 DTE cable) and the status of the physical layer of the interface. In above output we learn that there is an cable attached on S0/0 interface. If no cable is found we will see the line “No DTE cable” instead.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the best way to verify that a host has a path to other hosts in different networks?
A. Ping the loopback address.
B. Ping the default gateway.
C. Ping the local interface address.
D. Ping the remote network.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]While you were troubleshooting a connection issue, a ping from one VLAN to another VLAN on the same switch failed. Which command verifies that IP routing is enabled on interfaces and the local VLANs are up?
A. show ip interface brief
B. show ip nat statistics
C. show ip statistics
D. show ip route
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The “show ip nat statistics” only gives us information about NAT translation. We cannot know if IP routing is enabled or the VLANs are up not not.
The “show ip statistics” command does not exist.
With the “show ip interface brief” we can see if the interface VLANs are up or not but cannot see if IP routing is enabled or not. So let’s see what information can be learned with the “show ip route” command.
By using the command “show ip route” we will learn if IP routing is enabled. If it is not enabled we will see this output:
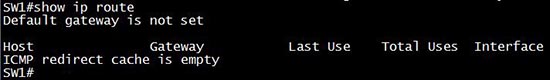
After enabling ip routing (via the “ip routing” in global configuration mode) we can see all the interfaces. For example:
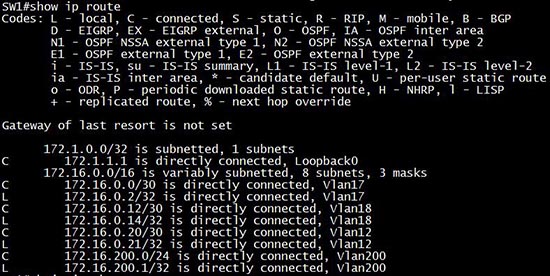
If we shut down an interface VLAN (Vlan18)
Sw1(config)#interface vlan 18
Sw1(config-if)#shutdown
then we will not see it in the routing table any more.
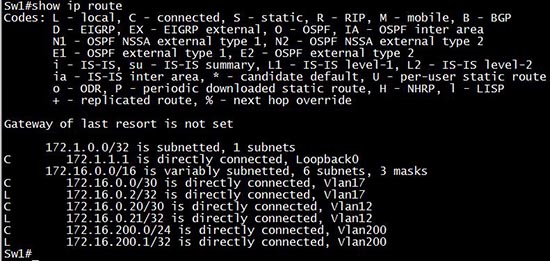
Therefore if the statement “local VLANs are up” means “the interface VLANs are up” then the “show ip route” is the best answer in this case.
Note: The IOS used to test is IOSv15.1
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command would you use on a Cisco router to verify the Layer 3 path to a host?
A. tracert address
B. traceroute address
C. telnet address
D. ssh address
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
To check the connectivity between a host and a destination (through some networks) we can use both “tracert” and “traceroute” commands. But the difference between these two commands is the “tracert” command can display a list of near-side router interfaces in the path between the source and the destination. The “traceroute” command has the same function of the “tracert” command but it is used on Cisco routers only, not on a PC -> B is correct.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]A network administrator has configured access list 173 to prevent Telnet and ICMP traffic from reaching a server with the address of 192.168.13.26. Which commands can the administrator issue to verify that the access list is working properly? (Choose three)
A. Router# ping 192.168.13.26
B. Router# debug access-list 173
C. Router# show open ports 192.168.13.26
D. Router# show access-lists
E. Router# show ip interface
Answer: A D E[/am4show]
Explanation
Answer B is not correct because “debug access-list ” command does not exist.
The reason answer E is correct because this command can help us see if the access-list was applied to the correct interface or not.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
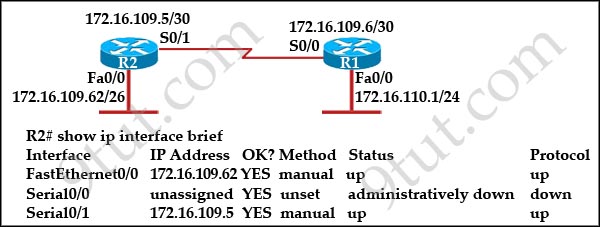
Assuming that the entire network topology is shown, what is the operational status of the interfaces of R2 as indicated by the command output shown?
A. One interface has a problem.
B. Two interfaces have problems.
C. The interfaces are functioning correctly.
D. The operational status of the interfaces cannot be determined from the output shown.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The subnet of Fa0/0 of R2 is 172.16.109.0/26 (range from 172.16.109.0 to 172.16.109.63) which covers the subnet of S0/1 interface 172.16.109.4/30 so in fact the answer C is not correct. But from the output of the “show ip interface brief” command we see both Fa0/0 and S0/1 interfaces’ statuses are ‘up/up’ -> they are working normally. So we think there is a typo in the subnet mask of Fa0/0. It should not be ‘/26’ but longer one, ‘/28’, for example. So you should still choose answer C in this question.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Hosts in network 192.168.2.0 are unable to reach hosts in network 192.168.3.0. Based on the output from RouterA, what are two possible reasons for the failure? (Choose two)
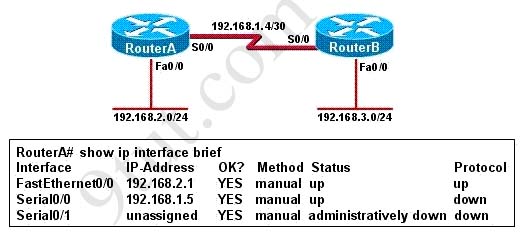
A. The cable that is connected to S0/0 on RouterA is faulty.
B. Interface S0/0 on RouterB is administratively down.
C. Interface S0/0 on RouterA is configured with an incorrect subnet mask.
D. The IP address that is configured on S0/0 of RouterB is not in the correct subnet.
E. Interface S0/0 on RouterA is not receiving a clock signal from the CSU/DSU.
F. The encapsulation that is configured on S0/0 of RouterB does not match the encapsulation that is configured on S0/0 of RouterA.
Answer: E F[/am4show]
Explanation
From the output we see the Serial0/0 of RouterA is in “status up/protocol down” state which indicates a Layer 2 problem so the problem can be:
+ Keepalives mismatch
+ Encapsulation mismatch
+ Clocking problem
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which interface counter can you use to diagnose a duplex mismatch problem?
A. runts
B. CRC errors
C. no carrier
D. late collisions
E. deferred
F. giants
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
At the end of each frame there is a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field. FCS can be analyzed to determine if errors have occurred. FCS uses cyclic redundancy check (CRC) algorithm to detect errors in the transmitted frames. Before sending data, the sending host generates a CRC based on the header and data of that frame. When this frame arrives, the receiving host uses the same algorithm to generate its own CRC and compare them. If they do not match then a CRC error will occur. CRC errors (and input errors in general) are often caused by duplex mismatch or Physical layer issues (like faulty cable, faulty network interface card or excessive interference during the transmission,…).
On an Ethernet connection, a duplex mismatch is a condition where two connected devices operate in different duplex modes, that is, one operates in half duplex while the other one operates in full duplex.
Note:
+ Runts are frames which do not meet the minimum frame size of 64 bytes. Runts are usually created by collisions.
+ Giants: frames that are larger than 1,518 bytes


Is question 3 right??
hich interface counter can you use to diagnose a duplex mismatch problem?
A. runts
B. CRC errors
C. no carrier
D. late collisions
E. deferred
F. giants
As i found on cisco and some other webpages, not CRC errors, but late collisions show us that there is a duplex missmatch issues. What is corect?
commonly cause LAN traffic congestion:
CRC errors with absence of colliosons and late collisions when there excessive noise and or
Cable damage on the link.
1. Too many hosts in a collision or broadcast domain
2. Broadcast storms – host experiences intermittent issues that relate to congestion
Broadcast Storm: ignored and no buffer number increase
3. Too much multicast traffic
4. Low bandwidth
5. Adding hubs for connectivity to the network
6. A bunch of ARP broadcasts
Duplex issuees
– Collisions are a normal occurrence in half-duplex operation.
Change the link to full-duplex to eliminate collisions.
– Late Collisions occur when there are problems in a switched network, duplex mismatch
– Typical duplex mismatch problems – full duplex side of link – high FCS errors
half duplex side high late collisons
verify the local IP stack you would ping the loopback 127.0.0.1
Excessive noise and
CRC accumulation
3 is wrong. D is a router command, you’re on a switch. A is correct.
show ip route is a switch command too
in real world CRC errors is an interface counter to diagnose a duplex mismatch problem. late collisions just a term.
some what confused Question 3 shows the output from a switch prompt but the “show ip route” is a router command.
Or is this been added to later versions of IOS
You just need to enable routing functionality on the switch using “IP routing” in config mode and you can use the sh ip route cmd
@anon I know you can run that command on a multi-layered switch but is not available on a layer 2 switch.
The question is not that clear but thanks for your input