New ICND2v3 Questions
Question 1
What is the default read-only (RO) mode of SNMP community string?
A. Public
B. Private
C. Cisco
D. Secret
Answer: A
Question 2
What is the output of the command “show snmp engineID”?
Answer: Local SNMP engineID and remote engineID
Question 3
Which protocol HSRP uses to interchange?
A. PPP
B. PPPoE
C. BPDU
D. Hello
Answer: D
Question 4
When does your enterprise require high-speed broadband internet?
A. P2P file sharing
B. Cloud computing
C. IaaS
D. vSAN expansion
E. upgrade IOS
F. resource-intensive application
Answer: B
Question 5
Responses from the TACACS+ daemon?
Answer: ACCEPT, REJECT, ERROR, CONTINUE
Question 6
What protocol CGMP is NOT compatible with?
A. HSRPv1
B. HSRPv2
Answer: A
Explanation
HSRPv1 uses the multicast address 224.0.0.2 to send hello packets, which can conflict with Cisco Group Management Protocol (CGMP) leave processing. You cannot enable HSRPv1 and CGMP at the same time; they are mutually exclusive.
Question 7
Which about GRE tunnel is true?
Answer: sends in plain text
Question 8
Which algorithm routing protocols are using?
Answer:
+ Dijkstra -> OSPF
+ Bellman-Ford -> RIP
+ DUAL -> EIGRP
Question 9
Which command is used to remove VLANs from trunk?
Answer: switchport trunk allowed vlan remove <VLANs>
Question 10
Which command is used to configure IPv6 peer for BGP?
Answer: neighbor xxxx remote-as xxxx
Question 11
Which command is used to verify GRE tunnel connectivity?
Answer: (not sure but maybe) traceroute OR “show tunnel interface tunnel <tunnel-ID>”
=============================New Questions added on 12nd-Feb-2018=============================
Question 12
Which of the following provide the highest availability?
A. full mesh
B. partial mesh
C. hub and spoke
Answer: A
Question 13
What can MPLS provide? (Choose two)
A. Authentication Header
B. secure payload of packet with ESP
C. VPN
D. CoS
Answer: A C
Question 14
Which ACL rules are applied as first?
A. Port filter
B. Router filter
C. VLAN filter
D. MAC filter
Answer: A
Explanation
In merge mode, the ACLs are applied in the following order:
1. PACL for the ingress port
2. VACL for the ingress VLAN
3. VACL for the egress VLAN
Port ACLs are similar to Router ACLs but are supported on physical interfaces and configured on Layer 2 interfaces on a switch. Port ACL supports only inbound traffic filtering. Port ACL can be configured as three type access lists: standard, extended, and MAC-extended
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=1181682&seqNum=4
Question 15
Which is true about IGP? (Choose two)
A. May use Bellman-Ford algorithm
B. May use Dijkstra Algorithm
C. Can be used between company and ISP
D. Can be used between router – Firewall – router
Answer: A B
Question 16 (maybe same as Question 9)
Which command will remove vlan 10 from trunk?
A. switchport trunk allowed vlan remove 10
B. switchport trunk allowed vlan add 10
C. switchport trunk allowed vlan except 10
Answer: A
Note: Another command to do this task is switchport trunk allowed vlan {all VLANS except 10}
Question 17
Troubleshooting connectivity between two devices. How will you start? (Choose two)
A. ping
B. extended ping with source
C. traceroute
D. something like connect to source’s next hop and do ping to destination
Answer: A C
Question 18
Which is true about keep-alive interval?
A. if was modified – should be equal on both side
B. have to apply on both side
Answer: A
Explanation
Since HDLC keepalives are ECHOREQ type keepalives, the keepalive frequency is important and it is recommended that they match up exactly on both sides. If the timers are out of sync, the sequence numbers start to get out of order. For example, if you set one side to 10 seconds and the other to 25 seconds, it will still allow the interface to remain up as long as the difference in frequency is not sufficient to cause the sequence numbers to be off by a difference of three.
Question 19
Which of the command enable PPP over Ethernet?
A. pppoe-client dial-pool-number
B. ppoe enable
Answer: B
Question 20
Which command immediately put port into forwarding state?
A. spanning-tree portfast default
B. spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
Answer: A
Explanation
Portfast is often configured on switch ports that connect to hosts. Interfaces with Portfast enabled will go to forwarding state immediately without passing the listening and learning state. Therefore it can save about 30 to 45 seconds to transition through these states.
To enable this feature, configure this command under interface mode:
Switch(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast
or we can use the spanning-tree portfast default global configuration command to globally enable the Port Fast feature on all nontrunking ports.
Question 21
Which feature can prevent switch to become Root Bridge?
A. VTP
B. DTP
C. Root Guard
C. BPDU Guard filter
Answer: C
Question 22
Which mode of VTP will only forward messages and ignore updates?
A. Client
B. Server
C. Transparent
Answer: C
Question 23
Which is correct about APIC-EM Path trace ACL? (Choose two)
A. It checks only ingress interface
B. It checks only egress interface
C. It checks ingress and egress interface
D. If finds ACL which deny traffic, will stop …
Answer: C and ?
Question 24
If TRAP in SNMP is not working, where can be issue?
A. Trap was not set
B. wasn’t put command “snmp-server enable traps”
C. SNMP server host has not configured inform messages
Answer: B
Explanation
Maybe this question wants to ask why TRAP is not sent after setting the trap.
If you do not enter an snmp-server enable traps command, no notifications controlled by this command are sent. In order to configure the router to send these SNMP notifications, you must enter at least one snmp-server enable traps command. If you enter the command with no keywords, all notification types are enabled. If you enter the command with a keyword, only the notification type related to that keyword is enabled. In order to enable multiple types of notifications, you must issue a separate snmp-server enable traps command for each notification type and notification option.
Note: For SNMP configuration please read https://www.9tut.com/simple-network-management-protocol-snmp-tutorial
Question 25
Which of the following two things does QOS provide? (Choose two)
Answer: checksum and inspection (not sure)
Question 26
Which of the following is true about Link state protocol?
Answer: (maybe) instant update
Question 27
Which of the following is true about Distance Vector?
Answer: (maybe) periodic update
Question 28
How can BGP advertise routes?
Answer: put command “network prefix mask DDN-mask”
Question 29
What is the default DTP mode?
A. Dynamic Desirable
B. Dynamic Auto
C. On
D. Off
Answer: B
Note: This question is same as Question 4 of https://www.9tut.net/icnd2-200-105/dtp-questions
Explanation
The Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) is used to negotiate forming a trunk between two Cisco devices.
In fact this question is unclear as it does not ask about a specific switch model. The default DTP configuration for Cisco Catalyst 2960 and 3560 switches is dynamic auto while older 3550 switches run Dynamic Desirable as the default mode. So in this question we should follow the “newer” switches (which is “dynamic auto” mode).
New switches are only set to “dynamic auto” mode by default so they are safer as they do not try to form a trunk aggressively.
Therefore in this question “dynamic auto” is the best choice.
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2181837&seqNum=8
Question 30
Which three options are benefits of using TACACS+ on a device? (Choose three)
A. It ensures that user activity is untraceable.
B. It provides a secure accounting facility on the device.
C. device-administration packets are encrypted in their entirely.
D. It allows the user to remotely access devices from other vendors.
E. It allows the users to be authenticated against a remote server.
F. It supports access-level authorization for commands.
Answer: C E F
Explanation
TACACS+ (and RADIUS) allow users to be authenticated against a remote server -> E is correct.
TACACS+ encrypts the entire body of the packet but leaves a standard TACACS+ header -> C is correct.
TACACS+ supports access-level authorization for commands. That means you can use commands to assign privilege levels on the router -> F is correct.
Note:
By default, there are three privilege levels on the router.
+ privilege level 1 = non-privileged (prompt is router>), the default level for logging in
+ privilege level 15 = privileged (prompt is router#), the level after going into enable mode
+ privilege level 0 = seldom used, but includes 5 commands: disable, enable, exit, help, and logout
Question 31
What prevents DDOS (Denial-of-service attack) attack?
Answer: DHCP snooping
Question 32
What allows two neighbor to establish EIGRP adjacency?
Answer: (recommended) same AS number, same subnet, same K values, same mask
Question 33
What command to check if a trunk is enable on an interface?
Answer: show int trunk
Question 34
What command will remove IPv6 OSPF address on an interface?
Answer: no ipv6 ospf 1 area x
Question 35
Why security of RADIUS may be compromised?
Answer: only the password is encrypted
Question 36
Which layer is ACL APIC-EM Path running on?
A. Layer 1
B. Layer 2
C. Layer 3
D. Layer 4
Answer: D
Question 37
What command will statically configure Etherchannel?
A. Desirable
B. Auto
C. On
D. Passive
Answer: C
Question 38
Which two options describe benefits of aggregated chassis technology? (Choose two)
A. It reduces management overhead
B. Switches can be located anywhere regardless of there physical location
C. It requires only one IP address per VLAN
D. It requires only three IP addresses per VLAN
E. It supports HSRP VRRP GLBP
F. It support redundant configuration files
Answer: A C
Explanation
Chassis aggregation is a Cisco technology to make multiple switches operate as a single switch. It is similar to stacking but meant for powerful switches (like the 6500 and 6800 series switches). Chassis aggregation is often used in the core layer and distribution layer (while switching stacking is used for access layer).
The books do not mention about the benefits of chassis aggregation but they are the same as switch stacking.
+ The stack would have a single management IP address.
+ The engineer would connect with Telnet or SSH to one switch (with that one management IP address), not multiple switches.
+ One configuration file would include all interfaces in all physical switches.
+ STP, CDP, VTP would run on one switch, not multiple switches.
+ The switch ports would appear as if all are on the same switch.
+ There would be one MAC address table, and it would reference all ports on all physical switches.
Reference: CCNA Routing and Switching ICND2 200-105 Official Cert Guide
VSS is a chassis aggregation technology but it is dedicated for Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches. VSS increases operational efficiency by simplifying the network, reducing switch management overhead by at least 50 percent -> A is correct
Single point of management, IP address, and routing instance for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 virtual switch
+ Single configuration file and node to manage. Removes the need to configure redundant switches twice with identical policies.
+ Only one gateway IP address is required per VLAN, instead of the three IP addresses per VLAN used today -> C is correct while D is not correct.
+ Removes the need for Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP), Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), and Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP)-> so maybe E is not correct.
Question 39
When troubleshooting client DNS issues, which two tasks must you perform? (Choose two)
A. Ping a public website IP address.
B. Ping the DNS Server.
C. Determine whether a DHCP address has been assigned.
D. Determine whether the hardware address is correct.
E. Determine whether the name servers have been configured
Answer: B E
Explanation
Complete these steps to troubleshoot this problem:
Ensure the router can reach the DNS server. Ping the DNS server from the router using its IP address, and make sure that the ip name-server command is used to configure the IP address of the DNS server on the router.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/domain-name-system-dns/24182-reversedns.html
Question 40
What routing protocol use first-hand information?
A. link-state
B. distance-vector
C. path-vector
D. other
Answer: A
Explanation
The information available to a distance vector router has been compared to the information available from a road sign. Link state routing protocols are like a road map. A link state router cannot be fooled as easily into making bad routing decisions, because it has a complete picture of the network. The reason is that unlike the routing-by-rumor approach of distance vector, link state routers have firsthand information from all their peer routers. Each router originates information about itself, its directly connected links, and the state of those links (hence the name). This information is passed around from router to router, each router making a copy of it, but never changing it. The ultimate objective is that every router has identical information about the internetwork, and each router will independently calculate its own best paths.
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=24090&seqNum=4
Question 41
Two features of the extended ping command? (Choose two)
A. It can send a specific number of packet
B. It can send packet from specified interface of IP address
C. It can resolve the destination host name
D. It can ping multiple host at the same time
Answer: A B
Explanation
There are many options to choose when using extended ping. Below shows the options that we can choose:
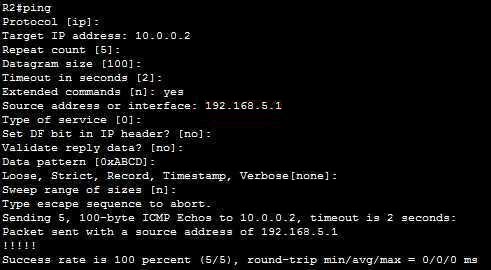
In which:
+ Repeat count [5]: Number of ping packets that are sent to the destination address. The default is 5 -> A is correct.
+ Source address or interface: The interface or IP address of the router to use as a source address for the probes -> B is correct.
For more information about extended ping, please read: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/routing-information-protocol-rip/13730-ext-ping-trace.html
Question 42
Which statement about IPv6 link-local addresses is true?
A. They must be configured on all IPv6 interface
B. They must be globally unique
C. They must be manually configured
D. They are advertised globally on the network
Answer: A
Explanation
Link-local addresses refer only to a particular physical link and are used for addressing on a single link for purposes such as automatic address configuration and neighbor discovery protocol. Link-local addresses can be used to reach the neighboring nodes attached to the same link. The nodes do not need a globally unique address to communicate. Routers will not forward datagram using link-local addresses. All IPv6 enabled interfaces have a link-local unicast address.
A link-local address is an IPv6 unicast address that can be automatically configured on any interface using the link-local prefix FE80::/10 (1111 1110 10) and the interface identifier in the modified EUI-64 format. Link-local addresses are not necessarily bound to the MAC address (configured in a EUI-64 format). Link-local addresses can also be manually configured in the FE80::/10 format using the “ipv6 address link-local” command.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/ip-version-6-ipv6/113328-ipv6-lla.html
In summary, if you do not configure a link-local on an IPv6 enabled interface, it will automatically use the FE80::/10 and the interface identifier in the modified EUI-64 format to form a link-local address.
Question 43
Which command can you enter on a switch to determine the current SNMP security model?
A. snmp-server contact
B. show snmp pending
C. show snmp group
D. show snmp engineID
Answer: C
Explanation
Three security models are available: SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3. The security model combined with the security level determine the security mechanism applied when the SNMP message is processed.
The command “show snmp group” displays the names of groups on the router and the security model, the status of the different views, and the storage type of each group. Below is an example of this command.
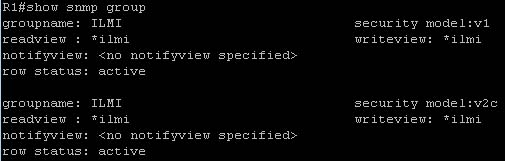
=========================New Questions added on 24th-Feb-2018============================
Question 44
What two options are causes of network slowness that can result from inter-VLAN routing problem? (Choose two)
A. Root guard disabled on an etherchannel
B. Packet Loss
C. DTP disabled on a switchport
D. BPDU guard enabled on a switchport
E. Hardware forwarding issues
Answer: B E
Explanation
Causes for Network Slowness
Packet Loss
In most cases, a network is considered slow when higher-layer protocols (applications) require extended time to complete an operation that typically runs faster. That slowness is caused by the loss of some packets on the network, which causes higher-level protocols like TCP or applications to time out and initiate retransmission.
Hardware Forwarding Issues
With another type of slowness, caused by network equipment, forwarding (whether Layer 2 [L2] or L3) is performed slowly. This is due to a deviation from normal (designed) operation and switching to slow path forwarding. An example of this is when Multilayer Switching (MLS) on the switch forwards L3 packets between VLANs in the hardware, but due to misconfiguration, MLS is not functioning properly and forwarding is done by the router in the software (which drops the interVLAN forwarding rate significantly).
Question 45
Which two commands debug a PPPoE connection that has failed to establish? (Choose two)
A. debug ppp compression
B. debug ppp negotiation
C. debug dialer events
D. debug ppp cbcp
E. debug dialer packet
Answer: B E
Explanation
According to this link https://supportforums.cisco.com/t5/network-infrastructure-documents/troubleshooting-for-pppoe-connection-failure-part-1/ta-p/3147204
The following debug commands can be used to troubleshoot PPPoE connection that failed:
+ debug ppp authentication
+ debug ppp negotiation
+ debug pppoe event
The debug ppp negotiation command enables you to view the PPP negotiation transactions, identify the problem or stage when the error occurs, and develop a resolution.
We are not sure about the “debug dialer packet” command but it seems to be the most reasonable answer left.
Question 46
Which command do you enter to determine wheter LACP is in use on a device?
A. Show port-channel summary
B. Show etherchannel summary
Answer: B
Question 47
Which three commands do you use to verify that IPsec over a GRE tunnel is working properly? (Choose three)
A. clear crpto iskamp
B. ppp encrypt mppe auto
C. show crypto engine connections active
D. show crypto ipsec sa
E. show crypto isakmp sa
F. debug crypto isakmp
Answer: D E F
Question 48
Which two types of cloud services may require you to alter the design of your network infrastructure? (Choose two)
A. Sudo as a service
B. Platform as a service
C. Infrastructure as a service
D. Software as a service
E. Business as a service
Answer: B C
Explanation
There are only three types of cloud services. These different types of cloud computing services delivery models are called
infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS).
Question 49
Which purpose of the network command in the BGP configuration of a router is true?
A. It enables route advertisement in the BGP routing process
B. It advertises any route in BGP with no additional configuration
C. It advertises a valid network as local to the autonomous system of a router
Answer: C
Question 50
Through with three states does a BGP routing process pass when it establishes a peering session?
A. open receive
B. inactive
C. active
D. connected
E. open sent
F. idle
Answer: C E F
Explanation
BGP forms a TCP session with neighbor routers called peers. The BGP session may report in the following states:
+ Idle
+ Connect
+ Active
+ OpenSent
+ OpenConfirm
+ Established
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2756480&seqNum=4
Question 51
Which encryption method does CHAP authentication use for the peer response?
A. EAP
B. MD5
C. DES
D. DSS
E. AES
F. 3DES
Answer: B
Question 52
Which two characteristics of stacked switches are true? (Choose two)
A. They reduce management complexity
B. They are less scalable than modular switches
C. They can manage multiple ip addresses across multiple switches
D. They have a single management interface
E. Each unit in the stack can be assigned its own IP address
Answer: A D
Question 53
Which option describes a drawback of proxy ARP?
A. It overwrites MAC addresses
B. It can make it more difficult for the administrator to locale device misconfigurations
C. It dynamically establishes layer 2 tunneling protocol which increase network overhead
D. If proxy ARP is configured on multiple devices , the internal L2 network may become vulnerable to DDOS
Answer: D
Question 54
Which layer 2 attack is specifically mitigated by changing the native VLAN to an unused VLAN?
A. Double tagging
B. DHCP spoofing
C. VLAN spoofing
D. switch hopping
Answer: A
Explanation
Let us learn about double-tagging attack.
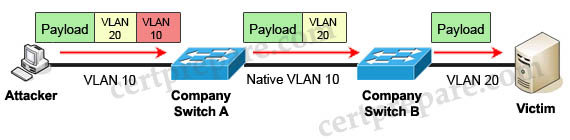
In double-tagging attack, the attacking computer generates frames with two 802.1Q tags. The first tag matches the native VLAN of the trunk port (VLAN 10 in this case), and the second matches the VLAN of a host it wants to attack (VLAN 20).
When the packet from the attacker reaches Switch A, Switch A only sees the first VLAN 10 and it matches with its native VLAN 10 so this VLAN tag is removed. Switch A forwards the frame out all links with the same native VLAN 10. Switch B receives the frame with an tag of VLAN 20 so it removes this tag and forwards out to the Victim computer.
Note: This attack only works if the trunk (between two switches) has the same native VLAN as the attacker.
According to this link http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2181837&seqNum=10
“The best approach to mitigating double-tagging attacks is to ensure that the native VLAN of the trunk ports is different from the VLAN of any user ports. In fact, it is considered a security best practice to use a fixed VLAN that is distinct from all user VLANs in the switched network as the native VLAN for all 802.1Q trunks.” -> Answer A is correct.
Question 55
Which feature or value must be configured to enable EIGRPv6?
Answer: Router id


is icnd2 200 105 the same as icnd2 v3
Yes aoli its the same, ICND 2 version is 3.
LOL @ Q14. Is Cisco really asking a CCIE-level question at the CCNA level? This justifies using dumps to study for their exams.
i need dump ccna 200-301