ICND2v3 – New Questions Part 7
Premium Members: You can practice these questions with our quizzes first at:
+ Question 1 to 20
+ Question 21 to 40
+ Question 41 to 60
+ Question 61 to 80
+ Question 81 to 102
Question 1
Which two statements about the Cisco APIC-EM ACL Path Trace feature are true? (Choose two)
A. Higher-priority ACEs override lower-priority ACEs in the same ACL.
B. The trace analyzes only the egress interface of all devices in the path.
C. The trace analyzes the ingress interface and the egress interface of all devices in the path.
D. The trace analysis stops as soon as the trace encounters a deny entry on the path.
E. The trace analyzes only the ingress interface of all devices in the path.
Answer: A C
Explanation
Access Control List (ACL) Trace analyzes how a flow is affected by ACLs programmed on the path. After the path is calculated between the source and the destination, the ACL Trace analyzes both ingress and egress interfaces of all devices on the path -> C is correct.
Analysis of entries within an individual ACL is cumulative. That is, if a higher priority ACE is a match, lower-priority ACEs are ignored -> A is correct.
Question 2
Which effect of the monitor session 16 source interface gigabitethernet 3/1 command is true?
A. It configures the device to monitor uni-directional source traffic for session 16.
B. It configures the device to monitor uni-directional destination traffic for session 16.
C. It configures the device interface as a source to monitor bi-directional traffic for session 16.
D. It configures the device interface as destination to monitor bi-directional traffic for session 16.
Answer: C
Explanation
Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) feature copies network traffic from a VLAN or group of ports to a selected port. SPAN is generally referred to as Port mirroring. An example of configuring SPAN port is shown below:
| Switch(config)#monitor session 1 source interface FastEthernet 0/1 Switch(config)#monitor session 1 destination interface FastEthernet 0/2 |
The above configuration will capture all traffic from interface FastEthernet 0/1 and send it to interface FastEthernet 0/2.
By default, both incoming and outgoing traffic is monitored.
Question 3
Which two benefits of using MPLS for WAN access are true? (Choose two)
A. It supports hub-and-spoke connectivity.
B. It supports CoS.
C. It provides VPN support.
D. It provides payload security with ESP.
E. It supports Authentication Header.
Answer: B C
Question 4
Which BGP command do you enter to allow a device to exchange IPv6 prefixes with its neighbor?
A. neighbor ip-address activate
B. neighbor ip-address remote-as ASN
C. router bgp ASN
D. show ip bgp neighbors
Answer: A
Question 5
For which type of connection is broadband PPPoE most appropriate?
A. satellite
B. DSL
C. GRE tunnel
D. PPTP
Answer: B
Explanation
PPPoE is commonly used in a broadband aggregation, such as by digital subscriber line (DSL). PPPoE provides authentication with the CHAP or PAP protocol.
Question 6
While troubleshooting the failure of an OSPFv3 Ethernet connection between routers R1 and R2, you determine that the hello timers are mismatched and that R2 is configured with default settings. Which command do you enter on R1 to correct the problem?
A. R1(config-if)#ipv6 ospf hello-interval 20
B. R1(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 10
C. R1(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 20
D. R1(config-if)#no ipv6 ospf hello-interval
Answer: D
Explanation
The default hello interval of OSPFv3 is 10 seconds when using Ethernet and 30 seconds when using nonbroadcast. To change the hello interval of OSPFv3, we use the “ipv6 ospf hello-interval seconds” command. Or we can use the “no” form to reset the hello timers to the default values.
Note: Answer B is not correct as it is for IPv4 OSPF, not IPv6 OSPF (should be “ipv6 ospf hello-interval 10, not “ip ospf hello-interval 10”)
Question 7
Which three statements about inform-request options are true? (Choose three)
A. The default number of retries is 3.
B. By default, the maximum number of pending informs is 10.
C. The default timeout is 60 seconds.
D. The default number of retries is 5.
E. The default timeout is 30 seconds.
F. By default, the maximum number of pending informs is 25.
Answer: A E (?) F
Explanation
SNMP inform-request. To specify inform request options, use the snmp-server inform [ pending pending ] [ retries retries ] [ timeout seconds ] command in global configuration mode.
The default value of “retries” is 3.
The default value of “timeout” is 15 seconds -> answer E is not correct but we don’t have any better choice.
The default value of “pending” is 25 (Number of unacknowledged informs to hold).
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/snmp/command/nm-snmp-cr-book/nm-snmp-cr-s5.html
Question 8
Which switch port mode prevents DTP frames from being sent?
A. trunk
B. dynamic auto
C. dynamic desirable
D. nonegotiate
Answer: D
Explanation
Disable DTP with the “switchport nonegotiate” so that DTP messages are not advertised out of the interface is also a good way to prevent auto trunking.
Question 9
Which difference between PVST+ and RPVST+ is true?
A. RPVST+ is based on 802.1D and PVST+ is based on 802.1s.
B. RPVST+ is based on 802.1w and PVST+ is based on 802.1s.
C. RPVST+ has slower convergence than PVST+.
D. Only PVST+ includes Cisco proprietary standards.
Answer: B
Explanation
RPVST+ is the Cisco’s version of RSTP that also uses PVST+ and provides a separate instance of 802.1w per VLAN.
Note: 802.1w is also called Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
PVST+ is the Cisco proprietary enhancement for STP that provides a separate 802.1d spanning-tree instance for each VLAN.
Question 10
When troubleshooting an issue with an SVI, which three areas do you check? (Choose three)
A. frame size
B. routing
C. interfaces
D. ASIC
E. gateway
F. encapsulation
Answer: B C E
Question 11
Which command do you enter to configure local authentication for PPP on a Cisco device?
A. router(config-if)#ppp authentication chap callin
B. router(config)#username router password password1
C. router(config-if)#ppp authentication chap
D. router(config-if)#ppp chap password password1
Answer: C
Question 12
Which three statements are benefits of using a shadow router as the source of IP SLA measurements? (Choose three)
A. It offsets the resource load from a production router.
B. It can be managed independently of production network traffic.
C. It reduces traffic through existing interfaces by adding another network interface.
D. It provides a better estimation of Layer 2 network traffic.
E. It enables switched traffic to take precedence over local traffic.
F. It adds an NTP synchronization point.
Answer: A B D
Question 13
When a user attempts to authenticate with TACACS+, which three responses from the TACACS+ daemon are possible? (Choose three)
A. PERSIST
B. FAULT
C. CONTINUE
D. ERROR
E. ACCEPT
F. REPEAT
Answer: C D E
Explanation
The network access server will eventually receive one of the following responses from the TACACS+ daemon:
+ ACCEPT – The user is authenticated and service may begin. If the network access server is configured to requite authorization, authorization will begin at this time.
+ REJECT – The user has failed to authenticate. The user may be denied further access, or will be prompted to retry the login sequence depending on the TACACS+ daemon.
+ ERROR – An error occurred at some time during authentication. This can be either at the daemon or in the network connection between the daemon and the network access server. If an ERROR response is received, the network access server will typically try to use an alternative method for authenticating the user.
+ CONTINUE – The user is prompted for additional authentication information.
Question 14
Which three statements about QoS policing are true? (Choose three)
A. It can be applied to outbound traffic only.
B. It avoids queuing delays.
C. It drops excess packets.
D. It can be applied to inbound and outbound traffic.
E. It queues excess traffic.
F. It is configured in bits per second.
Answer: B C D
Explanation
Unlike traffic shaping, QoS policing avoids delays due to queuing.
QoS policing drops (or remarks) excess packets above the committed rates. Does not buffer.
QoS policing is configured in bytes (while QoS traffic shaping is configured in bits per second)
QoS policing can be applied to both inbound and outbound traffic (while QoS shaping can only be applied to outbound traffic)
Question 15
Which three states are the HSRP stages for a router? (Choose three)
A. standby
B. speak
C. secondary
D. listen
E. learn
F. primary
Answer: A B D E (?)
Explanation
HSRP consists of 6 states:
| State | Description |
| Initial | This is the beginning state. It indicates HSRP is not running. It happens when the configuration changes or the interface is first turned on |
| Learn | The router has not determined the virtual IP address and has not yet seen an authenticated hello message from the active router. In this state, the router still waits to hear from the active router. |
| Listen | The router knows both IP and MAC address of the virtual router but it is not the active or standby router. For example, if there are 3 routers in HSRP group, the router which is not in active or standby state will remain in listen state. |
| Speak | The router sends periodic HSRP hellos and participates in the election of the active or standby router. |
| Standby | In this state, the router monitors hellos from the active router and it will take the active state when the current active router fails (no packets heard from active router) |
| Active | The router forwards packets that are sent to the HSRP group. The router also sends periodic hello messages |
Please notice that not all routers in a HSRP group go through all states above. In a HSRP group, only one router reaches active state and one router reaches standby state. Other routers will stop at listen state.
In this question there are four correct answers so maybe in the exam one correct answer would not exists but you should grasp the concept behind it.
Question 16
Which statement about link-state and distance-vector routing protocols is true?
A. Unlike distance-vector routing protocols, link-state routing protocols can cause routing loops.
B. Distance-vector routing protocols converge more quickly than link-state routing protocols.
C. Distance-vector routing protocols use more memory than link-state routing protocols.
D. Unlike distance-vector routing protocols, link-state routing protocols send routing-table updates to neighbors only after adjacency is established.
Answer: D
Question 17
Which three statements about the ACEs that are matched by a Cisco APIC-EM ACL path are true? (Choose three)
A. If the trace fails to find a matching ACE in an ACL, it is reported as implicitly permitted.
B. If an optional criterion is omitted from the trace, the results include all possible ACE matches.
C. If the trace fails to find a matching ACE in an ACL, it is reported as implicitly denied.
D. ACEs are reported only if they match.
E. All ACEs found by the trace are reported, including those that fail to match.
F. If an optional criterion is omitted from the trace, the results are reported as if the default value was specified.
Answer: B C D
Explanation
The following rules effect the ACL path trace results:
+ Only matching access control entry (ACE) are reported.
+ If you leave out the protocol, source port, or destination port when defining a path trace, the results include ACE matches for all possible values for these fields (-> These are optional criterion and if they are omitted, all possible results are included)
+ If no matching ACEs exists in the ACL, the flow is reported to be implicitly denied (-> It is same as an access-list, which always has an implicit “deny all” statement at the end)
Question 18
Which command do you enter to permit IPv6 functionality on an EIGRPv3 interface?
A. Router1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
B. Router1(config-if)#ipv6 router eigrp 1
C. Router1(config-if)#ipv6 enable
D. Router1(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1
Answer: D
Explanation
An example of configuring EIGRPv3 is shown as below:
| R1(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 1 R1(config-rtr)#router-id 1.1.1.1 R1(config-rtr)#no shutdown R1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 R1(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1 |
This question asks about “on an EIGRPv3 interface” so it is the only command this is required on an EIGRPv3 interface.
Question 19
Which command do you enter to create an SVI?
A. switch(config)#interface vlan 5
B. switch(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/5
C. switch(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/0.5
D. switch(vlan)#interface svi vlan 5
Answer: A
Question 20
Which command do you enter to protect a PortFast-enabled port against unauthorized switches on the network?
A. switch(config)#spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default
B. switch(config)#spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
C. switch(config-if)#spanning-tree guard root
D. switch(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast
Answer: B
Explanation
The BPDU guard feature can be globally enabled on the switch or can be enabled per port, but the feature operates with some differences.
At the global level, you enable BPDU guard on Port Fast-enabled ports by using the spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default global configuration command. Spanning tree shuts down ports that are in a Port Fast-operational state if any BPDU is received on them. In a valid configuration, Port Fast-enabled ports do not receive BPDUs. Receiving a BPDU on a Port Fast-enabled port means an invalid configuration, such as the connection of an unauthorized device, and the BPDU guard feature puts the port in the error-disabled state. When this happens, the switch shuts down the entire port on which the violation occurred.
Question 21
Which VTP operating mode enables a switch to forward VTP information while ignoring synchronization?
A. off
B. server
C. transparent
D. client
Answer: C
Question 22
Which switch architecture is scalable, flexible, resilient, and relatively inexpensive?
A. aggregate switch
B. single switch
C. stacked switch
D. modular-chassis switch
Answer: C
Explanation
Some network switches have the ability to be connected to other switches and operate together as a single unit. These configurations are called stacks, and are useful for quickly increasing the capacity of a network.
Stackable switches can be added or removed from a stack as needed without affecting the overall performance of the stack. Depending on its topology, a stack can continue to transfer data even if a link or unit within the stack fails. This makes stacking an effective, flexible, and scalable solution to expand network capacity.
Question 23
Which technology can prevent client devices from arbitrarily connecting to the network without state remediation?
A. 802.1x
B. IP Source Guard
C. MAC Authentication Bypass
D. 802.11n
Answer: A
Question 24
Which routing protocol is most appropriate for sending and receiving routes directly to and from the Internet?
A. RIP
B. BGP
C. EIGRP
D. OSPF
Answer: B
Question 25
Which command do you enter to configure client authentication for PPPoE?
A. Dev1(config-if)#ppp pap sent-username cisco password password1
B. Dev1(config)#aaa authentication ppp default local
C. Dev1(config-if)#ppp chap password password1
D. Dev1(config)#username cisco password password1
Answer: D
Question 26
Which two factors can affect the price of leased point-to-point WAN links? (Choose two)
A. amount of bandwidth used
B. type of traffic
C. amount of bandwidth requested
D. number of sites interconnected
E. distance between two points
Answer: A E
Question 27
In which LACP channel mode can the port initiate negotiations with other switch ports?
A. auto
B. active
C. desirable
D. passive
Answer: B
Question 28
To troubleshoot a network connection, you execute the ping utility on a route and it returns the response code Q. Which symptom is a probable root cause?
A. The ICMP time was exceed.
B. The destination is unreachable.
C. The connection timed out awaiting the reply.
D. The destination is receiving too much traffic.
Answer: D
Explanation
The table below lists the possible output characters from the ping facility:
| Character | Description |
|---|---|
| ! | Each exclamation point indicates receipt of a reply. |
| . | Each period indicates the network server timed out while waiting for a reply. |
| U | A destination unreachable error PDU was received. |
| Q | Source quench (destination too busy). |
| M | Could not fragment. |
| ? | Unknown packet type. |
| & | Packet lifetime exceeded. |
Question 29
Which two encapsulation types can use the keepalive command to monitor the link state of a WAN serial interface? (Choose two)
A. PPP
B. LMI
C. Frame Relay
D. HDLC
E. LCP
Answer: A D
Explanation
The keepalive command applies to serial interfaces that use High-Level Data Link Contol (HDLC) or PPP encapsulation. It does not apply to serial interfaces that use Frame Relay encapsulation.
For both PPP and HDLC encapsulation types, a keepalive of zero disables keepalives and is reported in the show running-config command output as keepalive disable.
Question 30
Which tool or utility can report whether traffic matching specific criteria can reach a specified destination on the ACLs along the path?
A. Cisco Security Device Manager
B. Cisco Prime
C. APIC-EM
D. Cisco Network Assistant
Answer: C
Explanation
If you performed an ACL trace, the devices show whether the traffic matching your criteria would be permitted or denied based on the ACLs configured on the interfaces.
Question 31
Which type of VPN allows for one endpoint to be learned dynamically during tunnel negotiation?
A. DMVPN
B. site-to-site VPN
C. GRE
D. client VPN
Answer: A
Question 32
Which function is performed by a TACACS+ server?
A. It hosts an access list that permits or denies IP traffic to the control plane of a device.
B. It provides external AAA verification.
C. It filters usernames and passwords for Telnet and SSH.
D. It serves as a database for line passwords.
Answer: B
Question 33
What do SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 have in common?
A. They use the same authentication techniques.
B. They both use the local database to permit username access.
C. They both protect against message tampering in transit.
D. They both encrypt packets.
Answer: A
Explanation
Both SNMPv1 and v2 did not focus much on security and they provide security based on community string only. Community string is really just a clear text password (without encryption). Any data sent in clear text over a network is vulnerable to packet sniffing and interception.
SNMPv3 provides significant enhancements to address the security weaknesses existing in the earlier versions. The concept of community string does not exist in this version. SNMPv3 provides a far more secure communication using entities, users and groups.
Question 34
Which three features are QoS congestion-management tools? (Choose three)
A. PPPoE
B. PQ
C. FIFO
D. PPP
E. PDQ
F. WFQ
Answer: B C F
Explanation
Good reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/qos_conmgt/configuration/xe-3s/qos-conmgt-xe-3s-book/qos-conmgt-oview.html
Question 35
Which two statements about exterior gateway routing protocols are true? (Choose two)
A. BGP is considered to be a path-vector protocol.
B. They can be used to connect to another AS across the Internet as a virtual instance.
C. eBGP is considered to be a distance-vector protocol.
D. EGP is considered to be a path-vector protocol.
E. They can be used to connect to the Internet.
Answer: A E
Question 36
Which two characteristics of a link-state routing protocol are true? (Choose two)
A. It sends periodic updates.
B. It has a higher CPU requirement than distance-vector protocols.
C. It supports a hop-count limit.
D. It receives updates on the multicast address.
E. It receives updates on the broadcast address.
Answer: B D
Question 37
Which statement about OSPFv3 configuration is true?
A. You can add networks under the routing process.
B. You must configure neighbors manually.
C. You must individually add interface IP addresses to the OSPFv3 database.
D. You can enable OSPFv3 for a network under the interface configuration mode.
Answer: D
Question 38
In which three circumstances may your organization require a high-bandwidth Internet connection? (Choose three)
A. It uses cloud computing
B. It uses network devices that require frequent IOS upgrades
C. It uses peer-to-peer file sharing
D. It is undergoing a SAN expansion
E. It uses Infrastructure as a Service
F. It uses resource-intensive applications
Answer: A C E
Question 39
After you notice that the SNMP manager is failing to receive traps, your troubleshooting verifies that the engine ID, username, group name, and host values are
set appropriately. Which configuration item is a probable root cause?
A. Traps are disabled.
B. The snmp-server enable traps command is missing from the configuration.
C. The snmp-server host informs command is missing from the configuration.
D. The host is down.
Answer: B
Question 40
In the Software-Defined Networking model, where is the interface between the control plane and the data plane?
A. between the control layer and the infrastructure layer
B. between the collocated layer and the dislocated layer
C. between the control layer and application layer
D. between the application layer and the infrastructure layer
Answer: A
Question 41
Which command do you enter so that a switch configured with Rapid PVST+ listens and learns for a specific time period?
A. switch(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 max-age 6
B. switch(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 hello-time 10
C. switch(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 4096
D. switch(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 forward-time 20
Answer: D
Explanation
The forward delay is the time that is spent in the listening and learning state. This time is equal to 15 sec by default, but you can tune the time to be between 4 and 30 sec.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/19120-122.html
Question 42
Which three protocols does APIC-EM support with Path Trace? (Choose three)
A. HSRP
B. ECMP
C. WLC
D. SNMP
E. SMTP
F. ECMP/TR
Answer: A B F
Explanation
Path Trace Supported Device Protocols and Network Connections:
Access Control List (ACL)
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN)
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
Equal Cost Multipath/Trace Route (ECMP/TR)
Equal Cost Multi Path (ECMP)
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) Protocol
…
For more information about these supported protocols and network connections, please visit https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/cloud-systems-management/application-policy-infrastructure-controller-enterprise-module/1-3-x/config-guide/b_apic-em_config_guide_v_1-3-x/b_apic-em_config_guide_v_1-3-x_chapter_0111.html
Question 43
Which step must you perform first to enable OSPFv3 process 20 for IPv6?
A. Enter the ipv6 router ospf 20 command to enable OSPFv3.
B. Enter the ip routing command to enable IPv4 unicast routing.
C. Enter the router ospf 20 commands to enable OSPF.
D. Enter the ipv6 unicast-routing command to enable IPv6 unicast routing.
Answer: D
Question 44
How can you mitigate VLAN hopping attacks?
A. Configure an unused nondefault VLAN as the native VLAN.
B. Enable dynamic ARP inspection.
C. Configure a used nondefault VLAN as the native VLAN.
D. Configure extended VLANs
Answer: A
Explanation
To mitigate VLAN Hopping, the following things should be done:
1) If no trunking is required, configure port as an access port, this also disables trunking on that interface:
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access
2) If trunking is required, try to configure the port to Nonegotiate to prevent DTP frames from being sent.
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
Switch(config-if)# switchport nonegotiate
3) Set the native VLAN to an unused VLAN and don’t use this VLAN for any other purpose (-> Therefore answer A is correct)
Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan VLAN-ID
4) Force the switch to tag the native VLAN on all its 802.1Q trunks:
Switch(config)# vlan dot1q tag native
Question 45
Which two statements about CHAP are true? (Choose two)
A. The CHAP negotiation phase begins after the LCP phase is complete.
B. Each authenticating router has a unique username and password.
C. It uses a three-way handshake to identify the peer router.
D. The local MD5 secret is transmitted to the peer for authentication.
E. The LCP phase begins after CHAP authentication is complete.
Answer: A C
Explanation
After the LCP (Link Control Protocol) phase is complete, and CHAP is negotiated between both devices, the authenticator sends a challenge message to the peer.
Question 46
After you configure multiple point-to-point tunnels on one interface, you notice that the interface is suffering from saturation. Which action do you take to correct the problem?
A. set the tunnel mode
B. set the bandwidth value
C. set the tunnel key argument
D. set the keepalive period
Answer: B
Question 47
Which two traffic types must always be transmitted on VLAN 1? (Choose two)
A. UDP
B. DTP
C. NTP
D. CDP
E. TCP
Answer: B D
Explanation
Control plane traffic (like CDP, VTP, STP…) runs on VLAN 1 by default. We cannot move these protocols to another VLAN.
Question 48
Which command can you enter to display the default VLAN?
A. show interface brief
B. show run
C. show ip interface brief
D. show interface f0/2 switchport
Answer: D
Explanation
An example of the “show interface e0/0 switchport” command is shown below:
Name: Et0/0 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Negotiation of Trunking: On Access Mode VLAN: 100 (VLAN0100) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled Voice VLAN: none Administrative private-vlan host-association: none Administrative private-vlan mapping: none Administrative private-vlan trunk native VLAN: none Administrative private-vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled Administrative private-vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q Administrative private-vlan trunk normal VLANs: none Administrative private-vlan trunk associations: none Administrative private-vlan trunk mappings: none Operational private-vlan: none Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Pruning VLANs Enabled: 2-1001 Capture Mode Disabled Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL Appliance trust: none
This command dispalys the default access mode VLAN & native VLAN.
Question 49
Which STP mode supports spanning-tree interoperability between Cisco and non-Cisco switches?
A. MSTP
B. PVST+
C. PVSTP
D. RSTP
Answer: B
Explanation
PVST: Cisco has a proprietary version of STP that offers more flexibility than the CST version. Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) operates a separate instance of STP for each individual VLAN. This allows the STP on each VLAN to be configured independently, offering better performance and tuning for specific conditions.
Cisco has a second proprietary version of STP that allows devices to interoperate with both PVST and CST. Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+) effectively supports three groups of STP operating in the same campus network:
+ Catalyst switches running PVST
+ Catalyst switches running PVST+
+ Switches running CST over 802.1Q
To do this, PVST+ acts as a translator between groups of CST switches and groups of PVST switches. PVST+ can communicate directly with PVST by using ISL trunks. To communicate with CST, however, PVST+ exchanges BPDUs with CST as untagged frames over the native VLAN. BPDUs from other instances of STP (other VLANs) are propagated across the CST portions of the network by tunneling. PVST+ sends these BPDUs by using a unique multicast address so that the CST switches forward them on to downstream neighbors without interpreting them first. Eventually, the tunneled BPDUs reach other PVST+ switches where they are understood.
Reference: CCNP SWITCH Official Certification Guide
In short, PVST+ supports interoperability between CST switches (run on non-Cisco devices) and PVST switches (run on Cisco devices)
Question 50
Where must you configure switch-level global features on a switch stack?
A. on the stack master
B. on the stack master and each individual stack member
C. on the stack master or any individual stack member
D. on each individual stack member
Answer: A
Question 51
Which HSRP feature do you configure so that the device with the highest priority immediately becomes the active router?
A. standby timers
B. preemption
C. standby authentication
D. holdtime
Answer: B
Question 52
Which Cisco IOS feature can you use to dynamically identify a connectivity problem between a Cisco device and a designated endpoint?
A. traceroute
B. ICMP Echo IP SLAs
C. IP SLAs threshold monitoring
D. Multi Operation Scheduler IP SLAs
Answer: B
Question 53
Which command must you enter to prepare an interface to carry voice traffic?
A. Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode access
B. Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
C. Switch1(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10
D. Switch1(config-if)#switchport host
Answer: B (?)
Explanation
In fact only old switches require a trunk to carry voice traffic. Modern switches can carry voice traffic in access mode.
Question 54
Which command do you enter to verify an SVI?
A. show running-configuration | include vlan5
B. show vlan5
C. show interface vlan5
D. show startup-configuration | include vlan5
Answer: C
Explanation
An SVI is nearly the same as an physical interface (except it is virtual and dedicated for a VLAN) so we can check it with the “show interface <vlan-id>” or “show ip interface <vlan-id>” command.
Question 55
What two options are causes of network slowness that can result from inter-VLAN routing problems? (Choose two)
A. Root guard disabled on an EtherChannel
B. Packet loss
C. DTP disabled on a switchport
D. BPDU guard enabled on a switchport
E. Hardware forwarding issues
Answer: B E
Explanation
Causes for Network Slowness
Packet Loss
In most cases, a network is considered slow when higher-layer protocols (applications) require extended time to complete an operation that typically runs faster. That slowness is caused by the loss of some packets on the network, which causes higher-level protocols like TCP or applications to time out and initiate retransmission.
Hardware Forwarding Issues
With another type of slowness, caused by network equipment, forwarding (whether Layer 2 [L2] or L3) is performed slowly. This is due to a deviation from normal (designed) operation and switching to slow path forwarding. An example of this is when Multilayer Switching (MLS) on the switch forwards L3 packets between VLANs in the hardware, but due to misconfiguration, MLS is not functioning properly and forwarding is done by the router in the software (which drops the interVLAN forwarding rate significantly).
Question 56
Which command do you enter to determine the root priority?
A. Show spanning-tree mapping
B. Show spanning-tree summary
C. Show spanning-tree bpdu-filter 1
D. Show spanning-tree backbonefast
Answer: B (?) in fact there is no correct answer
Explanation
The “show spanning-tree summary” command displays all the features that are enabled for STP (which includes PortFast BPDU Guard, Loop Guard, Root Guard); this command also displays the number of blocked, listening, learning, and forwarding interfaces. But it does not show the root priority. Other answers are not correct either.
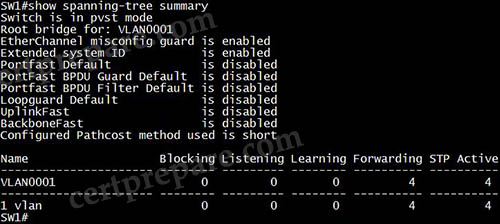
Question 57
Which two commands debug a PPPoE connection that has failed to establish? (Choose two)
A. Debug ppp compression
B. Debug ppp negotiation
C. Debug dialer events
D. Debug ppp cbcp
E. Debug dialer packet
Answer: B E
Question 58
Which two commands debug a PPPoE connection that has failed to establish? (Choose two)
A. debug ppp compression
B. debug ppp negotiation
C. debug dialer events
D. debug ppp cbcp
E. debug dialer packet
Answer: B E
Explanation
According to this link https://supportforums.cisco.com/t5/network-infrastructure-documents/troubleshooting-for-pppoe-connection-failure-part-1/ta-p/3147204
The following debug commands can be used to troubleshoot PPPoE connection that failed:
+ debug ppp authentication
+ debug ppp negotiation
+ debug pppoe event
The debug ppp negotiation command enables you to view the PPP negotiation transactions, identify the problem or stage when the error occurs, and develop a resolution.
We are not sure about the “debug dialer packet” command but it seems to be the most reasonable answer left.
Question 59
Which command do you enter to verify that a VLAN has been removed from a trunk?
A. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan none
B. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk except vlan 10
C. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk remove vlan 10
D. Switch(config-if)# no switchport trunk allowed vlan add 10
Answer: B (?)
Explanation
The command “switchport trunk allowed vlan none” remove all allowed VLANs on a trunk while the “switchport trunk except vlan <vlan-id>” will remove only the <vlan-id> out of the allowed VLAN list. But the question asks about verification so it is a bit unclear.
Question 60
Which command do you enter to determine whether LACP is in use on a device?
A. Show etherchannel summary
B. Show port-channel summary
C. Show etherchannel load-balance
D. Show ip protocols
Answer: B
Question 61
Which channel mode is available to static EhterChannels?
A. On
B. Passive
C. Active
D. Desirable
Answer: A
Question 62
Which three commands do you use to verify that IPSec over a GRE tunnel is working properly? (Choose three.)
A. Clear Crypto isakmp
B. PPP encrypt mppe auto
C. Show crypto engine connections active
D. Show crypto ipsec sa
E. Show crypto isakmp sa
F. Debug crypto isakmp
Answer: D E F
Question 63
Which combination of values is valid for a router-on-a-stick implementation?
A. IP address 173.15.20.6/20, gateway 173.15.30.1, and VLAN 20
B. FastEhernet interface 0/0.30, IP address 173.15.20.33/27, gateway 173.15.20.1 and VLAN 30
C. IP address 173.15.30.6/26, gateway 173.15.30.62, and VLAN 20
D. FastEthernet interface 0/0.20, IP address 173.15.30.33/27, gateway 173.15.30.1 and VLAN 30
Answer: C
Explanation
The gateway and the IP address of the subinterface must be in the same subnet -> only answer C is correct.
Question 64
Which two types of cloud services may require you to alter the design of your network infrastructure? (Choose two)
A. Sudo as a Service
B. Platform as a Service
C. Infrastructure as a Service
D. Software as a Service
E. Business as a Service
Answer: B C
Explanation
These different types of cloud computing services delivery models are called infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS).
Question 65
Through which three states does a BGP routing process pass when it establishes a peering session with a neighbor? (Choose three)
A. Open receive
B. Inactive
C. Active
D. Connected
E. Open sent
F. Idle
Answer: C E F
Explanation
BGP forms a TCP session with neighbor routers called peers. The BGP session may report in the following states:
+ Idle
+ Connect
+ Active
+ OpenSent
+ OpenConfirm
+ Established
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2756480&seqNum=4
Question 66
Which encryption method does CHAP authentication use for the peer response?
A. EAP
B. MD5
C. DES
D. DSS
E. AES
F. 3DES
Answer: B
Question 67
Which two characteristics of stacked switches are true? (Choose two)
A. They reduce management complexity.
B. They are less scalable than modular switches.
C. They can manage multiple IP addresses across multiple switches.
D. They have a single management interface.
E. Each unit in the stack can be assigned its own IP address for administration.
Answer: A D
Question 68
Which option describes a drawback of proxy ARP?
A. It overwrites MAC addresses that were learned with inverse ARP.
B. It can make it more difficult for the administrator to locate device misconfigurations.
C. It dynamically establishes Layer 2 tunneling protocols, which increases network overhead.
D. If proxy ARP is configured on multiple devices, the internal Layer 2 network may become vulnerable to DDoS attacks.
Answer: D
Question 69
Which feature or value must be configured to enable EIGRPv6?
A. Network statement
B. Shutdown feature
C. Router ID
D. Remote AS
Answer: C
Question 70
Which command do you enter to enable local authentication for Multilink PPP on an interface?
A. Router(config-if)# l2tp authentication
B. Router(config)# username router password password1
C. Router(config-if)# ppp chap password password1
D. Router(config)#aaa authentication ppp default local
Answer: B
Question 71
Which options are the two differences between HSRP versions 1 and 2? (Choose two)
A. Only HSRP version 2 can be configured to use authentication.
B. Only HSRP version 2 sends hello packets to 224.0.0.2.
C. Only HSRP version 1 sends hello packets to IPv6 multicast address FF02::66.
D. Only HSRP version 1 can be configured with a group number of 4095.
E. Only HSRP version 2 can be configured with a group number of 4095.
F. Only HSRP version 2 sends hello packets to 224.0.0.102.
Answer: E F
Explanation
In HSRP version 1, group numbers are restricted to the range from 0 to 255. HSRP version 2 expands the group number range from 0 to 4095 -> E is correct.
HSRP version 2 uses the new IP multicast address 224.0.0.102 to send hello packets instead of the multicast address of 224.0.0.2, which is used by version 1 -> F is correct.
Question 72
Which component of an IPv6 OSPFv3 connection must be configured in IPv4 format?
A. Router ID
B. Primary interface
C. Neighbor address
D. Secondary interface
Answer: A
Question 73
Which protocol can be used between administrative domains?
A. IS-IS
B. EIGRP
C. BGP
D. OSPF
Answer: C
Explanation
BGP is an example of an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) which exchanges routing information between different autonomous systems.
BGP is a path vector protocol. Path vector protocol does not rely on the bandwidth of the links (like OSPF) or hop count (like RIP) or a group of parameters (like EIGRP). Path vector protocol relies on the number of autonomous systems it has to go through. In other words, it choose the path with least number of autonomous systems (shortest AS Path) to reach the destination, provided that the path is loop-free.
Question 74
For which reason can a GRE tunnel have an UP/DOWN status?
A. The tunnel source interface is UP.
B. A tunnel destination is undefined.
C. The tunnel destination address is routable via a route that is separate from the tunnel.
D. The tunnel has been shut down.
Answer: B
Explanation
Under normal circumstances, there are only three reasons for a GRE tunnel to be in the up/down state:
– There is no route, which includes the default route, to the tunnel destination address.
– The interface that anchors the tunnel source is down.
– The route to the tunnel destination address is through the tunnel itself, which results in recursion.
Question 75
Which utility do you use to view IP traffic that is switched through the router to locate errors in a TCP stream?
A. Wireshark
B. Packet debugging
C. Ethereal
D. Ping
E. Traceroute
Answer: B
Explanation
Cisco routers provide a basic method of viewing IP traffic switched through the router called packet debugging. Packet debugging enables a user to determine whether traffic is travelling along an expected path in the network or whether there are errors in a particular TCP stream. Although in some cases packet debugging can eliminate the need for a packet analyzer, it should not be considered a replacement for this important tool.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/troubleshooting/guide/tr1907.html
Question 76
Which command do you enter so that a port enters the forwarding state immediately when a PC is connected to it?
A. Switch(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
B. Switch(config)# spanning-tree portfast default
C. Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast trunk
D. Switch(config-if)#no spanning-tree portfast
Answer: B
Explanation
If there is a “spanning-tree portfast” answer then it will surely be a correct answer. If not then answer B is the most suitable one even though the “spanning-tree portfast default” command enables PortFast globally on all non-trunking ports, not a single port.
Question 77
Which information is provided by the output of the show snmp engineID command?
A. Information about remote SNMP engines on the network only.
B. Information about the local SNMP engine and remote SNMP engines that are configured on the device.
C. Information about SNMP users and SNMP groups in the network.
D. Information about the local SNMP engine only.
Answer: B
Explanation
The “show snmp engineID” displays the identification of the local SNMP engine and all remote engines that have been configured on the router. The following example specifies 00000009020000000C025808 as the local engineID and 123456789ABCDEF000000000 as the remote engine ID, 171.69.37.61 as the IP address of the remote engine (copy of SNMP) and 162 as the port from which the remote device is connected to the local device:
Router# show snmp engineID Local SNMP engineID: 00000009020000000C025808 Remote Engine ID IP-addr Port 123456789ABCDEF000000000 171.69.37.61 162
Question 78
Which term represents the minimum bandwidth provided in a Metro Ethernet connection?
A. UNI
B. CIR
C. EVC
D. PIR
Answer: B
Explanation
Committed information rate (CIR): The minimum guaranteed data transfer rate agreed to by the routing device.
Question 79
What is the default value of the Read-Write-All-SNMP community string?
A. Secret
B. Private
C. Public
D. Cisco
Answer: A
Explanation
On Catalyst switches such as the 4000, 5000, and 6000 series that run a regular catalyst Operating System (OS), SNMP is enabled by default with the community strings set to:
+ Read-Only: Public
+ Read-Write: Private
+ Read-Write-all: Secret
With these community strings and the IP address of your switch’s management interface, anyone is able to reconfigure the device. You must change the community strings on the Catalyst switch immediately after you set the device on the network. This is very important.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/simple-network-management-protocol-snmp/7282-12.html
Question 80
Which three effects of using local SPAN are true? (Choose three)
A. It doubles the load on the forwarding engine.
B. It prevents SPAN destinations from using port security.
C. It doubles internal switch traffic.
D. It reduces the supervisor engine workload by half.
E. it reduces the load on the switch fabric.
Answer: A B C
Question 81
Refer to the exhibit.
| switch#configure terminal switch(config)#interface ethernet1/0 switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk switch(config-if)#switchport mode access switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10 |
Which option is the effect of this configuration?
A. It configures the switch port for trunk only.
B. It configures the switch port for voice traffic.
C. It configures the switch port for access and trunk.
D. It configures the switch port for access only.
Answer: D
Explanation
With this configuration, the first switchport command “switchport mode trunk” will be overwritten by the “switchport mode access” command and this port becomes an access port.
Question 82
Which command do you enter to allow a new VLAN across a trunk?
A. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk except vlan10
B. Switch(config-if)# no switchport trunk remove vlan10
C. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 10
D. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan10
Answer: C
Explanation
The command “switchport trunk allowed vlan add <vlan-id> adds a new VLAN to the previously allowed VLANs on the trunk. For example suppose our trunk is currently allowing VLANs 1, 4 ,5, 9, 12 then the command “switchport trunk allowed vlan add 10” will allow VLANs 1, 4 ,5, 9, 10, 12 on the trunk.
Question 83
Which feature can prevent a rogue device from assuming the role of the root bridge in a switching domain?
A. VTP
B. BPDU Filter
C. DTP
D. Root Guard
Answer: D
Explanation
Root Guard ensures that the port on which root guard is enabled is the designated port. If the bridge receives superior BPDUs on a root guard-enabled port, root guard moves this port to a root-inconsistent STP state (which is equal to STP listening state). No traffic is forwarded across this port. In this way, the root guard enforces the position of the root bridge.
Question 84
Which configuration do you apply to an HSRP router so that it is most likely to come up if the active router goes down?
A. Standby 4 preempt
B. Standby 4 priority 110 preempt delay 300
C. Standby 4 priority 115
D. Standby 4 priority 145
Answer: A
Question 85
In which two models can control-plane functionality be implemented? (Choose two)
A. Dispersed
B. Distributed
C. Fragmented
D. Centralized
E. Allocated
Answer: B D
Explanation
In its simplest form, the control plane provides layer-2 MAC reachability and layer-3 routing information to network devices that require this information to make packet forwarding decisions. In the case of firewalls, the control plane would include stateful flow information for inspection. Control plane functionality can implemented as follows:
+ Distributed – Conventional routers and switches operate using distributed protocols for control, i.e. where each device makes its own decisions about what to do, and communicate relevant information to other devices for input into their decision making process. For example, the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Fabric Path, and routing protocols such as IS-IS and BGP provide distributed control of packet forwarding functionality to networking devices.
+ Centralized – In this case, a centralized controller provides the necessary information for a network element to make a decision. For example, these controller(s) instruct networking devices on where to forward packets by explicitly programming their MAC and FIBs.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Data_Center/VMDC/SDN/SDN.html
Question 86
Which type of IPv6 ACL is applied first in the order of precedence?
A. TCAM
B. router ACLs
C. Fragmented frames
D. Port ACLs
Answer: D
Explanation
As with IPv4 ACLs, IPv6 port ACLs take precedence over router ACLs:
+ When an input router ACL and input port ACL exist in an SVI, packets received on ports to which a port ACL is applied are filtered by the port ACL. Routed IP packets received on other ports are filtered by the router ACL. Other packets are not filtered.
+ When an output router ACL and input port ACL exist in an SVI, packets received on the ports to which a port ACL is applied are filtered by the port ACL. Outgoing routed IPv6 packets are filtered by the router ACL. Other packets are not filtered.
Question 87
Which three fields can be marked with QoS? (Choose three)
A. Header checksum
B. IP precedence
C. DSCP
D. Total length
E. Discard Class
F. TTL
Answer: B C E
Explanation
For a single class, you can set operations on any two out of the following five fields: CoS, IP Precedence, DSCP, QoS Group, and Discard Class.
Question 88
Drag and drop the CSMA components from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right
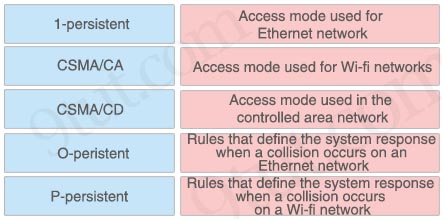
Answer:
+ 1-persistent: Access mode used for Ethernet network
+ CSMA/CA: Rules that define the system response when a collision occurs on a Wi-fi network
+ CSMA/CD: Rules that define the system response when a collision occurs on an Ethernet network
+ O-peristent: Access mode used in the controlled area network
+ P-persistent: Access mode used for Wi-fi networks
Explanation
1-persistent CSMA is an aggressive transmission algorithm. When the transmitting node is ready to transmit, it senses the transmission medium for idle or busy. If idle, then it transmits immediately. If busy, then it senses the transmission medium continuously until it becomes idle, then transmits the message (a frame) unconditionally (i.e. with probability=1). In case of a collision, the sender waits for a random period of time and attempts the same procedure again. 1-persistent CSMA is used in CSMA/CD systems including Ethernet.
Non persistent CSMA is a non aggressive transmission algorithm. When the transmitting node is ready to transmit data, it senses the transmission medium for idle or busy. If idle, then it transmits immediately. If busy, then it waits for a random period of time (during which it does not sense the transmission medium) before repeating the whole logic cycle (which started with sensing the transmission medium for idle or busy) again. This approach reduces collision, results in overall higher medium throughput but with a penalty of longer initial delay compared to 1–persistent.
P-persistent is an approach between 1-persistent and non-persistent CSMA access modes. [1]When the transmitting node is ready to transmit data, it senses the transmission medium for idle or busy. If idle, then it transmits immediately. If busy, then it senses the transmission medium continuously until it becomes idle, then transmits with probability p. If the node does not transmit (the probability of this event is 1-p), it waits until the next available time slot. If the transmission medium is not busy, it transmits again with the same probability p. This probabilistic hold-off repeats until the frame is finally transmitted or when the medium is found to become busy again (i.e. some other node has already started transmitting). In the latter case the node repeats the whole logic cycle (which started with sensing the transmission medium for idle or busy) again. p-persistent CSMA is used in CSMA/CA systems including Wi-Fi and other packet radio systems.
O-persistent
Each node is assigned a transmission order by a supervisory node. When the transmission medium goes idle, nodes wait for their time slot in accordance with their assigned transmission order. The node assigned to transmit first transmits immediately. The node assigned to transmit second waits one time slot (but by that time the first node has already started transmitting). Nodes monitor the medium for transmissions from other nodes and update their assigned order with each detected transmission (i.e. they move one position closer to the front of the queue).[2] O-persistent CSMA is used by CobraNet, LonWorks and the controller area network.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carrier-sense_multiple_access
Question 89
Drag and drop the PPPoE message types from the left into the sequence in which PPPoE messages are sent on the right.
| PADR | 1 |
| PADS | 2 |
| PADI | 3 |
| PADO | 4 |
Answer:
1. PADI
2. PADO
3. PADR
4. PADS
Question 90
Drag drop about characteristics of a cloud environment.
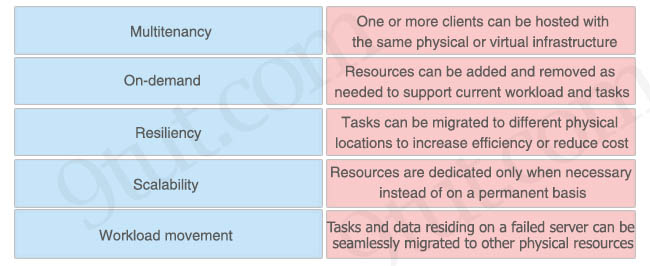
Answer:
+ Multitenancy: One or more clients can be hosted with the same physical or virtual infrastructure
+ Scalability: Resources can be added and removed as needed to support current workload and tasks
+ Workload movement: Tasks can be migrated to different physical locations to increase efficiency or reduce cost
+ On-demand: Resources are dedicated only when necessary instead of on a permanent basis
+ Resiliency: Tasks and data residing on a failed server can be seamlessly migrated to other physical resources
Question 91
Drag and drop the network programmability features from the left onto the correct description on the right.
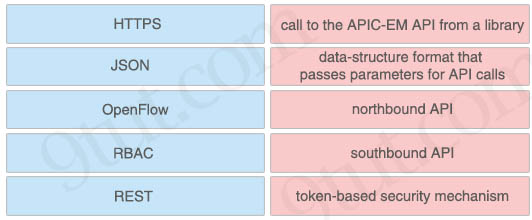
Answer:
+ HTTPS: call to the APIC-EM API from a library
+ JSON: data-structure format that passes parameters for API calls
+ OpenFlow: southbound API
+ RBAC: token-based security mechanism
+ REST: northbound API
Explanation
What is the data format used to send/receive data when making REST calls for APIC-EM?
Javascript Object Notation (JSON) is used to pass parameters when making API calls and is also the returned data format.
What’s RBAC?
The Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) mechanism utilizes security tokens that the controller issues upon successful authentication of a user of the APIC-EM controller. All subsequent requests from the authenticated user must provide a valid token.
Reference: https://communities.cisco.com/docs/DOC-60530#q16
Question 92
Drag and drop the descriptions of performing an initial device configuration from the left onto the correct features or components on the right.
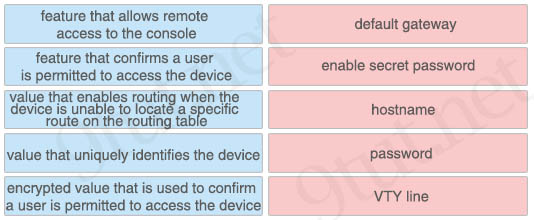
Answer:
+ feature that allows remote access to the console: VTY line
+ feature that confirms a user is permitted to access the device: password
+ value that enables routing when the device is unable to locate a specific route on the routing table: default gateway
+ value that uniquely identifies the device: hostname
+ encrypted value that is used to confirm a user is permitted to access the device: enable secret password
Question 93
Drag and drop the BGP components from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
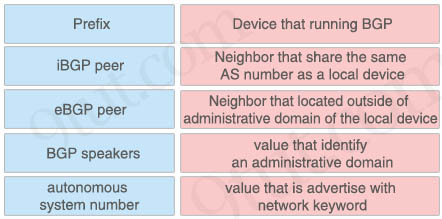
Answer:
+ autonomous system number: Value that identifies an administrative domain
+ BGP Speaker: device that is running BGP
+ eBGP: Peer neighbor that located outside of administrative domain of the local device
+ BGP Peer: neighbor device that shares the same AS number as the local device
+ Prefix: value that is advertised with the network keyword
Question 94
Which two QoS tools can provide congestion management? (Choose two)
A. CBWFQ
B. FRTS
C. CAR
D. PQ
E. PBR
Answer: A D
Explanation
This module discusses the types of queueing and queueing-related features (such as bandwidth management) which constitute the congestion management QoS features:
Class-based WFQ (CBWFQ): extends the standard WFQ functionality to provide support for user-defined traffic classes. For CBWFQ, you define traffic classes based on match criteria including protocols, access control lists (ACLs), and input interfaces. Packets satisfying the match criteria for a class constitute the traffic for that class.
Priority queueing (PQ): With PQ, packets belonging to one priority class of traffic are sent before all lower priority traffic to ensure timely delivery of those packets.
Note: Committed Access Rate (CAR) is only used for bandwidth limitation by dropping excessive traffic.
Question 95
Which two statements about EIGRP on IPv6 device are true? (Choose two)
A. It is configured on the interface
B. It is globally configured
C. It is configured using a network statement
D. It is vendor agnostic
E. It supports a shutdown feature
Answer: A E
Explanation
This is an example of how to configure EIGRP for IPv6:
| interface Serial0/0 no ip address ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ipv6 address 2010:AB8::1/64 ipv6 enable ipv6 eigrp 1 ! ipv6 router eigrp 1 eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2 no shutdown |
As you can see, EIGRP for IPv6 can only be enabled under each interface -> A is correct.
Under EIGRP process there is a shutdown feature where you can turn on or off -> E is correct.
Question 96
In which STP state does MAC address learning take place on a PortFast-enabled port?
A. learning
B. listening
C. discarding
D. forwarding
Answer: D
Explanation
PortFast-enabled port will ignore listening and learning state and jump to forwarding state immediately so it can only learn MAC addresses in this state.
Question 97
Which protocols does the internet layer in the tcp/ip model encapsulation? (Choose two)
A. smtp
B. tcp
C. arp
D. dns
E. icmp
F. udp
Answer: C E
Question 98
You notice that the packets that are sent from a local host to well-know service tcp port 80 of a remote host are sometimes lost you suspect an ACL issue. Which two APIC-EM path trace ACL-analysis options should you use to troubleshoot the problem? (Choose two)
A. protocol
B. debug
C. destination port
D. QoS
E. Performance monitor
Answer: A C
Question 99
Which IOS troubleshooting tool should yo use to direct system messages to your screen?
A. Local SPAN
B. Terminal monitor
C. APIC-EM
D. Log events
Answer: B
Question 100
In CDP environment what happens when the cdp interface on an adjacent device is configured without an IP address?
A. CDP becomes inoperable on that neighbor
B. CDP operates normally but it can cannot provide any information for that neighbor
C. CDP uses the ip address of another interface for that neighbor
D. CDP operates normally but it cannot provide ip address information for that neighbor
Answer: D
Question 101
Which two pieces of information about a Cisco device can Cisco Discovery Protocol communicate? (Choose two)
A. The native VLAN
B. The spanning tree protocol
C. The trunking protocol
D. The spanning tree priority
E. The VTP domain
Answer: A E
Explanation
The information contained in Cisco Discovery Protocol advertisements varies based on the type of device and the installed version of the operating system. Some of the information that Cisco Discovery Protocol can learn includes:
+ Cisco IOS version running on Cisco devices
+ Hardware platform of devices
+ IP addresses of interfaces on devices
+ Locally connected devices advertising Cisco Discovery Protocol
+ Interfaces active on Cisco devices, including encapsulation type
+ Hostname
+ Duplex setting
+ VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) domain
+ Native VLAN
Question 102
Drag drop about Administrative Distances of EIGRP and BGP.
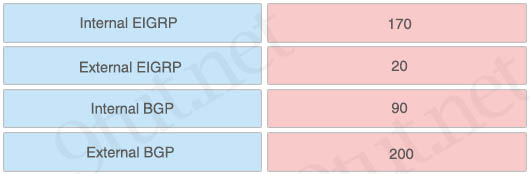
Answer:
+ Internal EIGRP – 90
+ External EIGRP – 170
+ Internal BGP – 200
+ External BGP – 20


F is not right for Q14 as QoS Policing token values are configured in Bytes, while Shaping is bits per seconds.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/quality-of-service-qos/qos-policing/19645-policevsshape.html
Question 14
Which three statements about QoS policing are true? (Choose three)
F. It is configured in bits per second
Answer to Q60 should be A (Show Etherchannel Summary)
no such command exists: Show Port-Channel.
instead, it has this command: Show Etherchannel Port-Channel
————————–
Question 60
Which command do you enter to determine whether LACP is in use on a device?
A. Show etherchannel summary
B. Show port-channel summary
C. Show etherchannel load-balance
D. Show ip protocols
Answer: B
hehe, again, it is me.
Answer B should be correct too.
these two commands are needed for the IPV6 EIGRP, and these two commands can only be configured in the global configuration mode.
”
IPV6 Uni-cast rouiting
IPV6 Router EIGRP 1
”
Question 95
Which two statements about EIGRP on IPv6 device are true? (Choose two)
A. It is configured on the interface
B. It is globally configured
C. It is configured using a network statement
D. It is vendor agnostic
E. It supports a shutdown feature
Answer: A E
based on my understanding, the Learning and listening states will be bypassed as long as the port is configured as PortFast and immediately go to the forwarding state, then how the switch learns the MAC address at LEARNING state (Answer A)
Question 96
In which STP state does MAC address learning take place on a PortFast-enabled port?
A. learning
B. listening
C. discarding
D. forwarding
has anyone taken the exam this month
have not taken it yet, would like to hear feedback from anyone who can say they actually saw some of these questions
this week, will definitely post something next monday.. !!!!
Hello, regarding question number 96. Shouldn’t it be D- Forwarding state as the portfast goes directly to forwarding state (D).
“PortFast causes a switch or trunk port to enter the spanning tree forwarding state immediately, bypassing the listening and learning states.”
“When the switch powers up, or when a device is connected to a port, the port enters the spanning tree listening state. When the Forward Delay timer expires, the port enters the learning state. When the Forward Delay timer expires a second time, the port is transitioned to the forwarding or blocking state.
When you enable PortFast on a switch or trunk port, the port is immediately transitioned to the spanning tree forwarding state.”
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4000/8-2glx/configuration/guide/stp_enha.html
@9tut for the question 96
The right answer is D, like anonymous june 30th said. The switch learn MAC addresses, based on received frames, at two states: Learning and Forwarding. In our case we don’t have the learning state because of portfast.
Question 70 got me confused.
Which command do you enter to enable local authentication for Multilink PPP on an interface?
A. Router(config-if)# l2tp authentication
B. Router(config)# username router password password1
C. Router(config-if)# ppp chap password password1
D. Router(config)#aaa authentication ppp default local
The suggested answer is B. However, the question specifically asks for configuration “on an interface”. Wouldn’t that imply that configuration prompt should be “Router(config-if)” ? And if that is the case, C is the only good option out of the two ( A or C ). What do others think?
@Grimraven I believe that because it doesn’t says nothing about configuration but instead specifically say enable local authentication. To enable it you must first have the B command. The A and D command is obviously wrong and the C command is for chap, which it’s not mentioned in the question
Can someone please explain Question 6 shown below? It says you are troubleshooting an OSPFv3 problem. And that the hello timers are changed from default values. But it says that R2 has default settings.
Since this is OSPFv3 (IPV6) why wouldnt the answer be to REMOVE the hello interval that was set with the NO ipv6 ospf hello-interval command (option D)
OSPFv3 is for ipv6 right? Why would the correct answer be showing an IPV4 command?
Answer D would remove the changed setting, and set it back to defaults. someone please explain how this is B, or hopefully, this is just a mistake in the question.
Question 6
While troubleshooting the failure of an OSPFv3 Ethernet connection between routers R1 and R2, you determine that the hello timers are mismatched and that R2 is configured with default settings. Which command do you enter on R1 to correct the problem?
A. R1(config-if)#ipv6 ospf hello-interval 20
B. R1(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 10
C. R1(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 20
D. R1(config-if)#no ipv6 ospf hello-interval
Answer: B
Explanation
The default hello interval of OSPFv3 is 10 seconds when using Ethernet and 30 seconds when using nonbroadcast.To change the hello interval of OSPFv3, we use the “ipv6 ospf hello-interval seconds” command.
Can anyone explain to me how Question 6 is B ? It says its an OSPFv3 issue. Answer B is not for OSPFv3, the only answer that makes sense to me is answer D, which would reset the value of the hello-timer back to defaults.
@Anonymous, @MosxarI: Yes, thanks for your detection, we have just updated Q.96
Question 89 on this page and on flash quiz have different answers
Passed ICND2 today with a 957. I only had 2 sims (ospf, eigrp) and NO CLI question which was weird. Lots of drag and drops. “New questions” parts 6 and 7 have 80+% of the questions I saw today. good luck all!
@mr pickles: Thanks for your detection, we have just updated Q.89
@Thank you 9tut! are perineum dumps are valid ??
So OSPF, EIGRP, and GRE tunnel are the SIM-s everybody had to do lately, ore did someone had other sims ??
Question 15
Why not LEARN?
Which three states are the HSRP stages for a router? (Choose three)
A. standby
B. speak
C. secondary
D. listen
E. learn
F. primary
Answer: A B D
Question 60
Which command do you enter to determine whether LACP is in use on a device?
A. Show etherchannel summary
B. Show port-channel summary
C. Show etherchannel load-balance
D. Show ip protocols
ANSWER: A is correct
#show etherchannel summary
——–
Number of channel-groups in use: 1
Number of aggregators: 1
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
——+————-+———–+———————————————–
1 Po1(SU) LACP Te1/1(P) Te1/2(P)
—————————————————-
tested it on Catalyst 4500 L3 Switch
Admin please update this page. Thank you
Question 14 ANSWER IS INCORRECT.
Which three statements about QoS policing are true? (Choose three)
A. It can be applied to outbound traffic only.
B. It avoids queuing delays.
C. It drops excess packets.
D. It can be applied to inbound and outbound traffic.
E. It queues excess traffic.
F. It is configured in bits per second. ( Shaping is in bits)
Answer: B C F X
CORRECT ANSWER: B. It avoids queuing delays.
C. It drops excess packets.
*D. It can be applied to inbound and outbound traffic.
read
Selection Criteria
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/quality-of-service-qos/qos-policing/19645-policevsshape.html
Admin, Please update this page.
Passed ICND Part 2 yesterday, scored 884. 54 questions. Studied all the icnd 2 content from 9tut.
question 15 —there is 4 correct answers??
Which three states are the HSRP stages for a router? (Choose three)
A. standby
B. speak
C. secondary
D. listen
E. learn
F. primary
Answer: A B D
Explanation
HSRP consists of 6 states:
State Description
Initial This is the beginning state. It indicates HSRP is not running. It happens when the
configuration changes or the interface is first turned on
Learn The router has not determined the virtual IP address and has not yet seen an
authenticated hello message from the active router. In this state, the router still waits
to hear from the active router.
Listen The router knows both IP and MAC address of the virtual router but it is not the active
or standby router. For example, if there are 3 routers in HSRP group, the router which
is not in active or standby state will remain in listen state.
Speak The router sends periodic HSRP hellos and participates in the election of the active or
standby router.
Standby In this state, the router monitors hellos from the active router and it will take the active
state when the current active router fails (no packets heard from active router)
Active The router forwards packets that are sent to the HSRP group. The router also sends
periodic hello messages
So will I be good if I study and learn the material in Part 6 and Part 7 and all the links in the main page under ” For ICND2 candidates:”
Question about PPPoe message types: are we sure the order is correct? seems like PADS and PADR are flipped. I think the order should be: PADI, PADO, PADS, PADR.
when I answer the question about using a shadow router as the source of IP SLA measurements, it only returns 2 correct answers when the question says pick 3. Are their only 2 correct answers, or is one answer not showing?
I just took the exam today, and this site is the best you can get for test prep. purchase the premium, and you are guaranteed to pass.
Hey kboogie, I test Monday and have been focused on New ICNDv3 Part 6, Part 7 and th Sims. How far back should I go?
@delriozaudio looks like there are three answers but the quiz is only counting two of them. If you look at the question out of the quiz there are three answers.
@delrioaudio here is a follow up. The question above is correct not the quiz. Here is why three answers is correct.
A dedicated router used as a source of IP SLA measurement is also called a shadow router. Implementing IP SLA with a shadow router has several advantages:
• Dedicated router would offset the resource load on production router from the implemented IP SLA Network Management operations
• Dedicated router would be a central device that can be independently managed without any impact on network traffic.
• Better estimation of Layer 2 switching performance can be obtained if the access port is placed on the same switch/linecard as the endpoint to be managed.
I just took this exam and in total saw about 5-7 questions from here. I think coming here is a good way to gauge what kind of questions you will be asked but not as a main study source. OH aand lotsss of drag and drop.
Good Luck!
p.s I got a 783 twice
Hi Guys,
Any update regarding the ICND2 exam ? Has anyone took the exam recently ?
Are questions still up to date ?
Thanks !
Hello All,
Please provide any input on taking the ICND2. I am taking my exam on 9/6. I been studying all the modules and parts 6 and 7… along with the sims. Please any information to help pass will be greatly appreciated.
I’m taking my test on the 13th, I’ll post back if these questions are any good or not, let’s hope so!
Does anyone else think these questions are ridiculously “out there” for an ASSOCIATE?
Other study materials I’m using:
Boson ICND2
TestOut
Cisco CCNA in 60 Days book
SYBEX CCNA R&S
@9/11 CCNA expires:
Please update with your exam outcome. Good Luck!!!!!
Question 25
Which command do you enter to configure client authentication for PPPoE?
A. Dev1(config-if)#ppp pap sent-username cisco password password1
B. Dev1(config)#aaa authentication ppp default local
C. Dev1(config-if)#ppp chap password password1
D. Dev1(config)#username cisco password password1
Answer: D
https://packetlife.net/blog/2009/apr/20/configuring-pppoe/
This one seems wrong to me. D is for LOCAL authentication. But i googled client aunthentication for PPPoE and the link i pasted shows the client end just needs the username and password for the ISP configured username and password. No need to configure client with it’s own local username.
Passed ICND2. Most of these questions are legit. There are tons of drag and drop questions and multiple guess (choose two out of the five) type questions.
The labs were really, really easy. OSPF and EIGRP.
Don’t use this website as your only resource.
Will this be enough to pass for a recertification?
Which configuration do you apply to an HSRP router so that it is most likely to come up if the active router goes down?
A. Standby 4 preempt
B. Standby 4 priority 110 preempt delay 300
C. Standby 4 priority 115
D. Standby 4 priority 145
I believe that should be D? In the case of an active router failing the one with the higher priority would win, since the negotiation has already triggered the preempt would be useless and would’t affect the negotiation at all.
@Donil are you took test in October and part 6 and 7 enough to pass?
Maybe I am seeing double, or I am going crazy.
A. IP address 173.15.20.6/20, gateway 173.15.30.1, and VLAN 20
B. FastEhernet interface 0/0.30, IP address 173.15.20.33/27, gateway 173.15.20.1 and VLAN 30
C. IP address 173.15.30.6/26, gateway 173.15.30.62, and VLAN 20
D. FastEthernet interface 0/0.20, IP address 173.15.30.33/27, gateway 173.15.30.1 and VLAN 30
Answer is C
However aren`t both answer A and C correct? And not only C?
A 173.15.20.6/20 has a range of 173.15.16.1 – 173.15.31.254, so the gateway address of 173.15.30.1 is within the address range.
C. IP address 173.15.30.6/26 has a range of 173.15.30.1 – 173.15.30.62, so the gateway address of 173.15.30.62 is also within range…
Often(in the real world?) addresses for router interfaces have the lowest IP or highest IP within a address range,
In case of C 173.15.30.1 and 173.15.30.62, but I am not sure if that is Cisco best practice or something, or that it is just something almost all people do(I think it is this one). So not sure about this one.
@ak08 no not at all. I failed my exam a week ago and came here to revise on some questions. I saw 2 of these question in my exam. Study before using dumps or leave networking as a whole. I studied 5 months ofr ICND2 and still failed,it happens but the fact is that I still did a hell load of input every night and day. Study for your knowledge, not your CV
peace brother.
This site is amazing! Studying for ICDN2 and taking it soon.
Can you send me the latest dumps for 200-105 ICND2 to:
Tran4cox @ hotmail.com
Any assistance would be much appreciated!
Best Regards,!
Question53: Answer should be A
Question 56. Which command do you enter to determine the root priority?
A. Show spanning-tree mapping
B. Show spanning-tree summary
C. Show spanning-tree bpdu-filter 1
D. Show spanning-tree backbonefast
Answer: B (?) in fact there is no correct answer
Actually I believe the correct answer is to use the “show spanning-tree root” command, or more specifically “show spanning-tree root priority” command
reference https://www.cisco.com/c/m/en_us/techdoc/dc/reference/cli/n5k/commands/show-spanning-tree-root.html
Just passed with an 835. Thanks 9tut.
I felt like there was alot of PPOE questions i didn’t know.
Hola mastapoohba solamente leiste esta 100 preguntas? para el ICND2?
mastapoohba what did you study for 9tut?
to pass the exam
passed ICND2! thanks 9tut!
passed ICND2! thanks 9tut!
many ask from here, labs OSPF and EIGRP from here
Passed ICND2 today with 920+, a lot of questions the same as on here. Some different answers so make sure to know the concepts. Simulations were pretty similar, I had EIGRP and OSPF, the only command you need is “Show IP Route” and “Show run”
I took it last week, got in the low 700s. I have a bunch of Cisco credits so I wasn’t expecting to pass this time. I saw a lot of the questions in ICND2v3 New Questions parts 6 and 7. Almost none from prior parts. Had I actually studied this site more carefully I would have probably passed. If I get the same test on my retake I will pass.
Of note, a few drag and drops, several labs, but no configuration – just troubleshooting. I was worried about the labs more than anything and those turned out to the easiest. I didn’t see a single question about port numbers or IPv6.
Passed exam 950+ Thanks for a great website. Explanations are spot on.
Passed exam today 930 + well worth the money. Perfect when used with other learning sources such as ine , Cisco books and YouTube . This website will just give you an idea of what the exam will be like the answers change slightly but if you did the studying you will pass . A lot of the new questions from 5 6 7 were on the exam.
You should do it before February as the questions are very unlikely to change. Good luck !!!
Passed exam today 910+ around 60% of the questions were from new questions 6 + 7. The simulations were very similar too. I had EIGRP and GRE Tunnels. Study along with this website and you’ll pass!!
Passed yesterday got 870 out 1000
54 Questions in total. If you are going to take the exam soon:
– EIGRP sim,OSPF sim same here on 9tut, word for word
– 10 questions Drag and Drop all in ICND2v3 – New Questions Part 6 & 7
– ALL the NEW questions here, THEY ARE ALL VALID
– ICND2v3 – New Questions Part 4 to 7 you’ll be fine
MANY THANKS TO 9TUT well done
just passed icnd2 with 965. All questions from 9 tut specially new questions part 6 and 7.
thanks a lot 9tut.
I took this twice (had some Cisco credits). After the 1st one I signed up for 9tut and found a lot of the same questions. Studied those. Took it again, but this version of the test had almost no 9tut questions. Maybe 5 out of 54. Ironically, I still passed. 860 suckers.
9tut is invaluable for preparing you for the type of questions you’re going to see, but there are 3+ versions of the test and at least one of those is NOT covered by this site.
None of the version I took (and I took 2) had questions on IPv6. I saw no questions on Administrative Distance or port numbers either. There were a lot of VLAN questions. After the 1st test I crammed my VLAN notes in addition to the 9tut questions and that’s what probably saved me. Study your VLANs!!! Also the labs are easy. Who would have thought.
Did anyone get a drag and drop where you had to match a pool of statements that you had to drag to the true side and some were left out? I missed passing by like 1-2 questions, so assistance would be helpful in case I get it again.
Question 59
Which command do you enter to verify that a VLAN has been removed from a trunk?
A. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan none
B. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk except vlan 10
C. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk remove vlan 10
D. Switch(config-if)# no switchport trunk allowed vlan add 10
Answer: B (?)
That has to be wrong because there is no such command in the Cisco OS.. (B,C)
In fact, the “closest” answer must be A. Because if you remove every VLAN from a Trunk, you have verified that there is no VLAN on a trunk. You get it? Seems funny, but cisco sometimes asks questions for fun i guess…
Answer does not make any sense so there is just one answer left..
@9tut please update this Question
To the post above:
Answer “D” does not make any sense so there is just one answer left..
————————————————————————————
Question 60
Which command do you enter to determine whether LACP is in use on a device?
A. Show etherchannel summary
B. Show port-channel summary
C. Show etherchannel load-balance
D. Show ip protocols
Answer: B (is not correct)
Explanation
There is no such command in the cisco OS
output:
SwitchA#show port-channel summary
^
% Invalid input detected at ‘^’ marker.
SwitchA#sh etherchannel summary
Flags: D – down P – bundled in port-channel
I – stand-alone s – suspended
H – Hot-standby (LACP only)
R – Layer3 S – Layer2
U – in use f – failed to allocate aggregator
M – not in use, minimum links not met
u – unsuitable for bundling
w – waiting to be aggregated
d – default port
Number of channel-groups in use: 1
Number of aggregators: 1
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
——+————-+———–+———————————————–
1 Po1(SU) LACP Gi1/0/25(P) Gi1/0/27(P) Gi1/0/28(D)
SwitchA#
Answer B is the correct answer!
Question 15
Which three states are the HSRP stages for a router? (Choose three)
A. standby
B. speak
C. secondary
D. listen
E. learn
F. primary
Correct Answer is B,D,E
@9TUT
Question 53
Which command must you enter to prepare an interface to carry voice traffic?
A. Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode access
B. Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
C. Switch1(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10
D. Switch1(config-if)#switchport host
I think correct Answer is A Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode access
Thanks
Hello guys cheers from Perú i passed my examn icnd2 885 points yesterday ando just see 15% new questions and the simulation it’s the same un topologic here but the answers it’s differente and drag and droop only 2 questions here, good look.
Hi guys and 9Tut staff, I got my membership recently and was checking the “ICND2v3 – New Questions” from part 1 to 8 and noticed that parts from 1 to 4 and maybe 5 as well are quite old (from 2018).
I am taking ICND2 very soon and was wondering if these old questions are still valid?, is still worth it to invest time in those parts from 1 to 5 or have they been deprecated?
Thanks for your time and effort to put this amazing resource together.
Checking is to report that I passed ICND2 today with 921. Minimum passing score 811. Studied with Wendall Odom’s exam guide, Cisco learning acadamy resources, and checked out “New Questions Parts 6-8” of this website. 80% of the questions on my exam were covered here.
Pass ICND1 2/14/20 with 859
6,7,8, and sim is all you need.
Good Luck!
I think I’m one of the last, who pass the old exam.
19/02/2020, ICND2, 933/1000
9tut is unbeatable …
Today 21/02/2020 I pass ICND2 with951 out of 1000 just wish to thank 9tut ,for fantastic study material, you are by far the best in the market