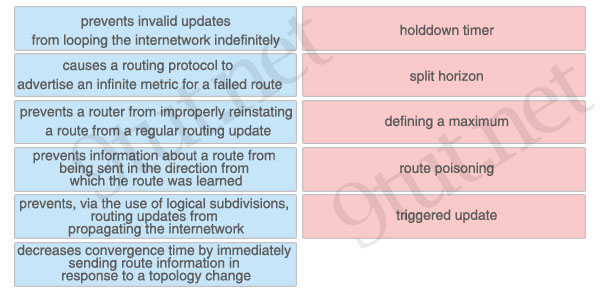
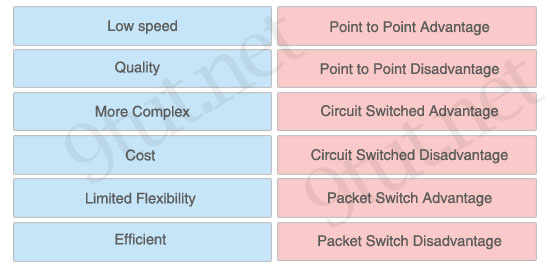
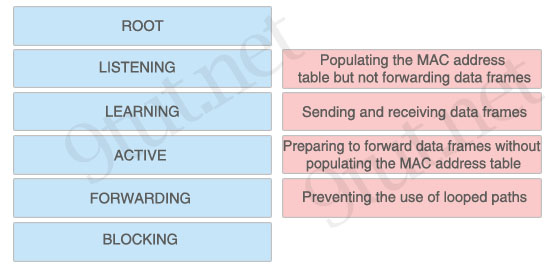
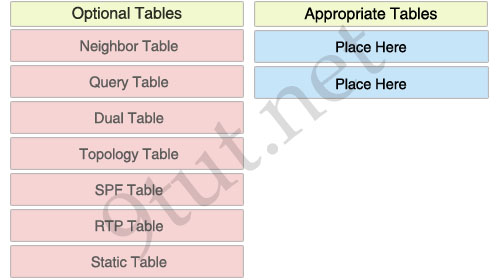
ICND1 – Miscellaneous Questions
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statements are true regarding ICMP packets? (Choose two)
A. They acknowledge receipt of TCP segments.
B. They guarantee datagram delivery
C. TRACERT uses ICMP packets.
D. They are encapsulated within IP datagrams.
E. They are encapsulated within UDP datagrams
Answer: C D[/am4show]
Explanation
Tracert (or traceroute) is used to trace the path between the sender and the destination host. Traceroute works by sending packets with gradually increasing Time-to-Live (TTL) value, starting with TTL value = 1. The first router receives the packet, decrements the TTL value and drops the packet because it then has TTL value zero. The router sends an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source. The next set of packets are given a TTL value of 2, so the first router forwards the packets, but the second router drops them and replies with ICMP Time Exceeded. Proceeding in this way, traceroute uses the returned ICMP Time Exceeded messages to build a list of routers that packets traverse, until the destination is reached and returns an ICMP Echo Reply message -> C is correct.
ICMP is encapsulated in an IP packet. In particular, the ICMP message is encapsulated in the IP payload part of an IP datagram -> D is correct.
Note: The TRACERT command on Windows Operating System uses ICMP while MAC OS X and Linux TRACEROUTE use UDP.
Question 2
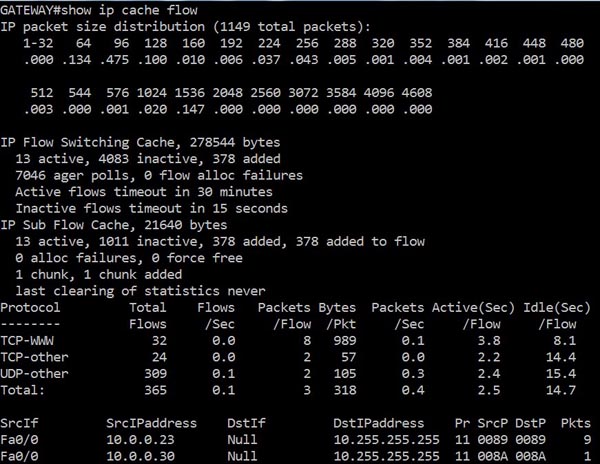
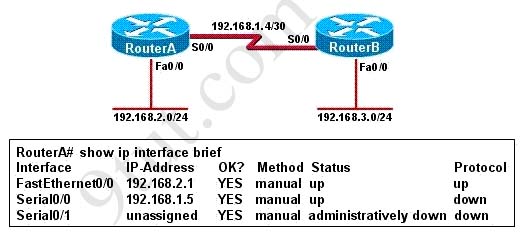
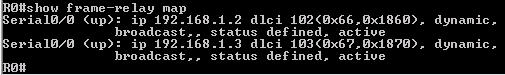
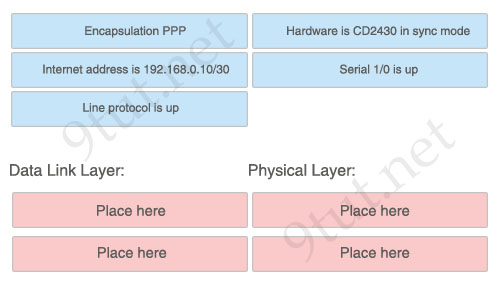
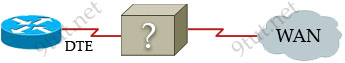
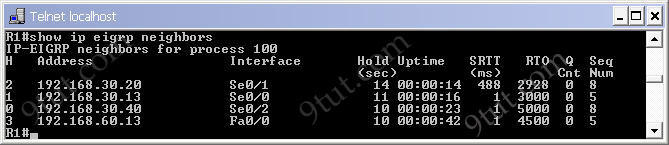
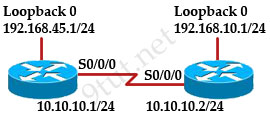
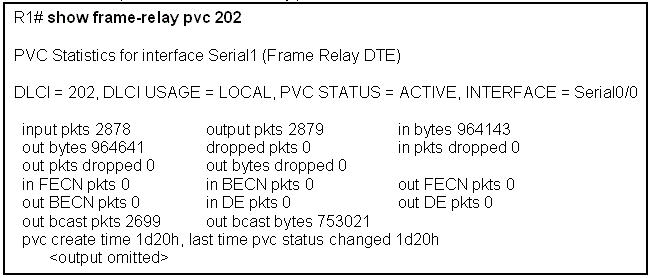
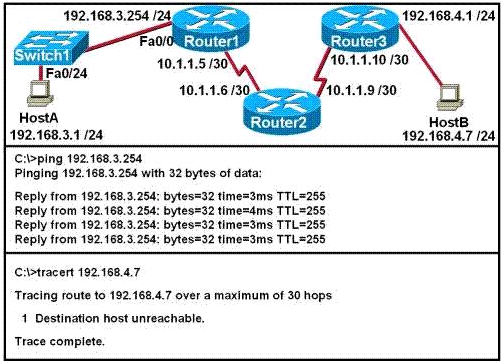
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. An administrator cannot connect from R1 to R2. To troubleshoot this problem, the administrator has entered the command shown in the exhibit. Based on the output shown, what could be the problem?
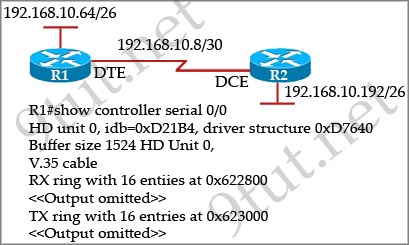
A. The serial interface is configured for half duplex.
B. The serial interface does not have a cable attached.
C. The serial interface has the wrong type of cable attached.
D. The serial interface is configured for the wrong frame size.
E. The serial interface has a full buffer.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The output above is unclear. Normally when we use this command we can see the type of serial connection on this interface, for example “V.35 DCE cable. Below is an example of the same command as above:
|
RouterA#show controllers serial 0 |
Or
|
RouterB#show controllers serial 0 |
but in this case we only get “V.35 cable”. So in fact we are not sure about the answer C. But the output above also does not have any information to confirm other answers are correct or not.
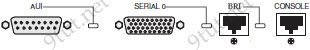
Just for your information, the V.35 male and V.35 female cable are shown below:


Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]How many simultaneous Telnet sessions does a Cisco router support by default?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
F. 6
Answer: E[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which of the following is a characteristic of full-duplex communication?
A. It is a CSMA/CD network.
B. It is a CSMA/CA network.
C. It is point-to-point only.
D. Hub communication is done via full duplex.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which set of conditions comprises a successful ping attempt between two connected routers configured with IP addresses on the same subnet?
A. The destination host receives an echo reply from the source host within one second and the source host receives an echo request from the destination host.
B. The destination host receives an echo request from the source host within one second.
C. The destination host receives an echo reply from the source host within one second and the source host receives an echo reply from the destination host within two seconds.
D. The destination host receives an echo request from the source host and the source host receives an echo request from the destination host within one second.
E. The destination host receives an echo request from the source host and the source host receives an echo reply from the destination host within two seconds.
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
The ping command first sends an echo request packet to an address, then waits for a reply. The ping is successful only if:
+ The echo request gets to the destination, and
+ The destination is able to get an echo reply back to the source within a predetermined time called a timeout. The default value of this timeout is two seconds on Cisco routers.